Keywords
COVID-19 pneumonia, deep vein thrombosis, venous thromboembolism, pulmonary embolism, heparin
Abstract
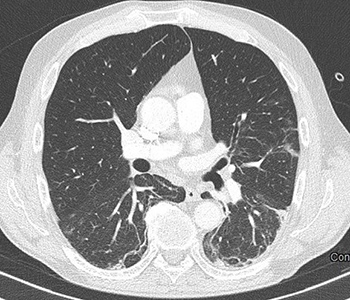
Coronavirus disease 19 (COVID-19) is a worldwide infection which was recently declared a global health emergency by the WHO Emergency Committee. The most common symptoms are fever and cough, which can progress to pneumonia, acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) and/or end-organ failure. Risk factors associated with ARDS and death are older age, comorbidities (e.g., hypertension, diabetes, hyperlipidaemia), neutrophilia, and organ and coagulation dysfunction. Disseminated intravascular coagulation and coagulopathy can contribute to death. Anticoagulant treatment is associated with decreased mortality in severe COVID-19 pneumonia. In this report we describe two patients with COVID-19 pneumonia who developed venous thromboembolism.
References
Views: 5058
HTML downloads: 432
PDF downloads: 2540
Published:
2020-04-08
Issue:
2020: Vol 7 No 5
(view)










