Abstract
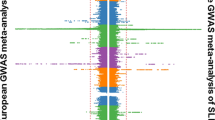
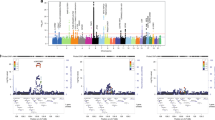
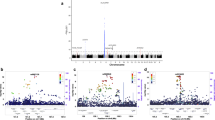
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a chronic autoimmune disorder characterized by inflammation of multiple organ systems and dysregulated interferon responses. SLE is both genetically and phenotypically heterogeneous, greatly reducing the power of case-control studies in SLE. Elevated circulating interferon-alpha (IFN-α) is a stable, heritable trait in SLE, which has been implicated in primary disease pathogenesis. About 40–50% of patients have high IFN-α, and high levels correspond with clinical differences. To study genetic heterogeneity in SLE, we performed a case−case study comparing patients with high vs low IFN-α in over 1550 SLE cases, including genome-wide association study and replication cohorts. In meta-analysis, the top associations in European ancestry were protein kinase, cyclic GMP-dependent, type I (PRKG1) rs7897633 (PMeta=2.75 × 10−8) and purine nucleoside phosphorylase (PNP) rs1049564 (PMeta=1.24 × 10−7). We also found evidence for cross-ancestral background associations with the ankyrin repeat domain 44 (ANKRD44) and pleckstrin homology domain containing, family F member 2 gene (PLEKHF2) loci. These loci have not been previously identified in case-control SLE genetic studies. Bioinformatic analyses implicated these loci functionally in dendritic cells and natural killer cells, both of which are involved in IFN-α production in SLE. As case-control studies of heterogeneous diseases reach a limit of feasibility with respect to subject number and detectable effect size, the study of informative pathogenic sub-phenotypes becomes an attractive strategy for genetic discovery in complex disease.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 6 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $19.83 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Harley JB, Kelly JA, Kaufman KM . Unraveling the genetics of systemic lupus erythematosus. Springer Semin Immunopathol 2006; 28: 119–130.
Ko K, Koldobskaya Y, Rosenzweig E, Niewold TB . Activation of the interferon pathway is dependent upon autoantibodies in African-American SLE patients, but not in European-American SLE patients. Front Immunol 2013; 4: 309.
Sanchez E, Comeau ME, Freedman BI, Kelly JA, Kaufman KM, Langefeld CD et al. Identification of novel genetic susceptibility loci in African American lupus patients in a candidate gene association study. Arthritis Rheum 2011; 63: 3493–3501.
Ko K, Franek BS, Marion M, Kaufman KM, Langefeld CD, Harley JB et al. Genetic ancestry, serum interferon-alpha activity, and autoantibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol 2012; 39: 1238–1240.
Niewold TB, Hua J, Lehman TJ, Harley JB, Crow MK . High serum IFN-alpha activity is a heritable risk factor for systemic lupus erythematosus. Genes Immun 2007; 8: 492–502.
Graham RR, Kozyrev SV, Baechler EC, Reddy MV, Plenge RM, Bauer JW et al. A common haplotype of interferon regulatory factor 5 (IRF5) regulates splicing and expression and is associated with increased risk of systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat Genet 2006; 38: 550–555.
Harley JB, Alarcon-Riquelme ME, Criswell LA, Jacob CO, Kimberly RP, Moser KL et al. Genome-wide association scan in women with systemic lupus erythematosus identifies susceptibility variants in ITGAM, PXK, KIAA1542 and other loci. Nat Genet 2008; 40: 204–210.
Remmers EF, Plenge RM, Lee AT, Graham RR, Hom G, Behrens TW et al. STAT4 and the risk of rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med 2007; 357: 977–986.
Gateva V, Sandling JK, Hom G, Taylor KE, Chung SA, Sun X et al. A large-scale replication study identifies TNIP1, PRDM1, JAZF1, UHRF1BP1 and IL10 as risk loci for systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat Genet 2009; 41: 1228–1233.
Rullo OJ, Tsao BP . Recent insights into the genetic basis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis 2013; 72 (Suppl 2): ii56–ii61.
Ghodke-Puranik Y, Niewold TB . Genetics of the type I interferon pathway in systemic lupus erythematosus. Int J Clin Rheumatol 2013; 8: 657–669.
Kim K, Brown EE, Choi CB, Alarcon-Riquelme ME, Kelly JA, Glenn SB et al. Variation in the ICAM1-ICAM4-ICAM5 locus is associated with systemic lupus erythematosus susceptibility in multiple ancestries. Ann Rheum Dis 2012; 71: 1809–1814.
Blanco P, Palucka AK, Gill M, Pascual V, Banchereau J . Induction of dendritic cell differentiation by IFN-alpha in systemic lupus erythematosus. Science 2001; 294: 1540–1543.
Hooks JJ, Moutsopoulos HM, Geis SA, Stahl NI, Decker JL, Notkins AL . Immune interferon in the circulation of patients with autoimmune disease. N Engl J Med 1979; 301: 5–8.
Weckerle CE, Franek BS, Kelly JA, Kumabe M, Mikolaitis RA, Green SL et al. Network analysis of associations between serum interferon-alpha activity, autoantibodies, and clinical features in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 2011; 63: 1044–1053.
Petri M, Singh S, Tesfasyone H, Dedrick R, Fry K, Lal P et al. Longitudinal expression of type I interferon responsive genes in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 2009; 18: 980–989.
Niewold TB, Clark DN, Salloum R, Poole BD . Interferon alpha in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Biomed Biotechnol 2010; 2010: 948364.
Niewold TB . Interferon alpha-induced lupus: proof of principle. J Clin Rheumatol 2008; 14: 131–132.
Niewold TB, Swedler WI . Systemic lupus erythematosus arising during interferon-alpha therapy for cryoglobulinemic vasculitis associated with hepatitis C. Clin Rheumatol 2005; 24: 178–181.
Kariuki SN, Kirou KA, MacDermott EJ, Barillas-Arias L, Crow MK, Niewold TB . Cutting edge: autoimmune disease risk variant of STAT4 confers increased sensitivity to IFN-alpha in lupus patients in vivo. J Immunol 2009; 182: 34–38.
Niewold TB, Kelly JA, Flesch MH, Espinoza LR, Harley JB, Crow MK . Association of the IRF5 risk haplotype with high serum interferon-alpha activity in systemic lupus erythematosus patients. Arthritis Rheum 2008; 58: 2481–2487.
Robinson T, Kariuki SN, Franek BS, Kumabe M, Kumar AA, Badaracco M et al. Autoimmune disease risk variant of IFIH1 is associated with increased sensitivity to IFN-alpha and serologic autoimmunity in lupus patients. J Immunol 2011; 187: 1298–1303.
Agik S, Franek BS, Kumar AA, Kumabe M, Utset TO, Mikolaitis RA et al. The autoimmune disease risk allele of UBE2L3 in African American patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: a recessive effect upon subphenotypes. J Rheumatol 2012; 39: 73–78.
Eliopoulos E, Zervou MI, Andreou A, Dimopoulou K, Cosmidis N, Voloudakis G et al. Association of the PTPN22 R620W polymorphism with increased risk for SLE in the genetically homogeneous population of Crete. Lupus 2011; 20: 501–506.
Mavragani CP, Niewold TB, Moutsopoulos NM, Pillemer SR, Wahl SM, Crow MK . Augmented interferon-alpha pathway activation in patients with Sjogren's syndrome treated with etanercept. Arthritis Rheum 2007; 56: 3995–4004.
Niewold TB, Wu SC, Smith M, Morgan GA, Pachman LM . Familial aggregation of autoimmune disease in juvenile dermatomyositis. Pediatrics 2011; 127: e1239–e1246.
Maiti AK, Kim-Howard X, Motghare P, Pradhan V, Chua KH, Sun C et al. Combined protein- and nucleic acid-level effects of rs1143679 (R77H), a lupus-predisposing variant within ITGAM. Hum Mol Genet 2014; 23: 4161–4176.
Kariuki SN, Franek BS, Kumar AA, Arrington J, Mikolaitis RA, Utset TO et al. Trait-stratified genome-wide association study identifies novel and diverse genetic associations with serologic and cytokine phenotypes in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Res Ther 2010; 12: R151.
Koldobskaya Y, Ko K, Kumar AA, Agik S, Arrington J, Kariuki SN et al. Gene-expression-guided selection of candidate loci and molecular phenotype analyses enhance genetic discovery in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Dev Immunol 2012; 2012: 682018.
Farkas L, Beiske K, Lund-Johansen F, Brandtzaeg P, Jahnsen FL . Plasmacytoid dendritic cells (natural interferon- alpha/beta-producing cells) accumulate in cutaneous lupus erythematosus lesions. Am J Pathol 2001; 159: 237–243.
Hagberg N, Berggren O, Leonard D, Weber G, Bryceson YT, Alm GV et al. IFN-alpha production by plasmacytoid dendritic cells stimulated with RNA-containing immune complexes is promoted by NK cells via MIP-1beta and LFA-1. J Immunol 2011; 186: 5085–5094.
Rullo OJ, Woo JM, Wu H, Hoftman AD, Maranian P, Brahn BA et al. Association of IRF5 polymorphisms with activation of the interferon alpha pathway. Ann Rheum Dis 2010; 69: 611–617.
Orstavik S, Natarajan V, Tasken K, Jahnsen T, Sandberg M . Characterization of the human gene encoding the type I alpha and type I beta cGMP-dependent protein kinase (PRKG1). Genomics 1997; 42: 311–318.
Snyder FF, Jenuth JP, Mably ER, Mangat RK . Point mutations at the purine nucleoside phosphorylase locus impair thymocyte differentiation in the mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1997; 94: 2522–2527.
Toro A, Grunebaum E . TAT-mediated intracellular delivery of purine nucleoside phosphorylase corrects its deficiency in mice. J Clin Invest 2006; 116: 2717–2726.
Lipsky PE . Systemic lupus erythematosus: an autoimmune disease of B cell hyperactivity. Nat Immunol 2001; 2: 764–766.
Sasaki Y, Iseki M, Yamaguchi S, Kurosawa Y, Yamamoto T, Moriwaki Y et al. Direct evidence of autosomal recessive inheritance of Arg24 to termination codon in purine nucleoside phosphorylase gene in a family with a severe combined immunodeficiency patient. Hum Genet 1998; 103: 81–85.
Markert ML . Purine nucleoside phosphorylase deficiency. Immunodefic Rev 1991; 3: 45–81.
Lee-Kirsch MA, Gong M, Chowdhury D, Senenko L, Engel K, Lee YA et al. Mutations in the gene encoding the 3'-5' DNA exonuclease TREX1 are associated with systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat Genet 2007; 39: 1065–1067.
Al-Mayouf SM, Sunker A, Abdwani R, Abrawi SA, Almurshedi F, Alhashmi N et al. Loss-of-function variant in DNASE1L3 causes a familial form of systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat Genet 2011; 43: 1186–1188.
Namjou B, Kothari PH, Kelly JA, Glenn SB, Ojwang JO, Adler A et al. Evaluation of the TREX1 gene in a large multi-ancestral lupus cohort. Genes Immun 2011; 12: 270–279.
Lin WJ, Yang CY, Lin YC, Tsai MC, Yang CW, Tung CY et al. Phafin2 modulates the structure and function of endosomes by a Rab5-dependent mechanism. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2010; 391: 1043–1048.
Li C, Liu Q, Li N, Chen W, Wang L, Wang Y et al. EAPF/Phafin-2, a novel endoplasmic reticulum-associated protein, facilitates TNF-alpha-triggered cellular apoptosis through endoplasmic reticulum-mitochondrial apoptotic pathway. J Mol Med (Berl) 2008; 86: 471–484.
Stefansson B, Ohama T, Daugherty AE, Brautigan DL . Protein phosphatase 6 regulatory subunits composed of ankyrin repeat domains. Biochemistry 2008; 47: 1442–1451.
Chio A, Schymick JC, Restagno G, Scholz SW, Lombardo F, Lai SL et al. A two-stage genome-wide association study of sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Hum Mol Genet 2009; 18: 1524–1532.
Kosoy R, Nassir R, Tian C, White PA, Butler LM, Silva G et al. Ancestry informative marker sets for determining continental origin and admixture proportions in common populations in America. Hum Mutat 2009; 30: 69–78.
Jabs WJ, Hennig C, Zawatzky R, Kirchner H . Failure to detect antiviral activity in serum and plasma of healthy individuals displaying high activity in ELISA for IFN-alpha and IFN-beta. J Interferon Cytokine Res 1999; 19: 463–469.
Hua J, Kirou K, Lee C, Crow MK . Functional assay of type I interferon in systemic lupus erythematosus plasma and association with anti-RNA binding protein autoantibodies. Arthritis Rheum 2006; 54: 1906–1916.
Feng X, Han D, Kilaru BK, Franek BS, Niewold TB, Reder AT . Inhibition of interferon-beta responses in multiple sclerosis immune cells associated with high-dose statins. Arch Neurol 2012; 69: 1303–1309.
Yeung KY, Ruzzo WL . Principal component analysis for clustering gene expression data. Bioinformatics 2001; 17: 763–774.
Purcell S, Neale B, Todd-Brown K, Thomas L, Ferreira MA, Bender D et al. PLINK: a tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am J Hum Genet 2007; 81: 559–575.
Whitlock MC . Combining probability from independent tests: the weighted Z-method is superior to Fisher's approach. J Evol Biol 2005; 18: 1368–1373.
Acknowledgements
Research reported in this publication was supported by the National Institutes of Health under award numbers: R01 AR060861 (NTB), UL1 RR024999 (NTB), K08 AI083790 (NTB), LRP AI071651 (NTB), N01 AR62277 (HJB), R3724717 (HJB), AR042460 (HJB), P01 AI083194 (HJB), P20 RR020143 (HJB), R01 DE018209 (HJB), R01 AR043274 (SKL), R01 CA141700 (ARME), RC1 AR058621 (ARME), RO1 AR43814 (TBP), P60 AR053308 (CLA), R01 AR44804 (CLA) and UL1 TR000004. Additional support was granted from the HHMI Gilliam Fellowship for Advanced Study (KSN), Alliance for Lupus Research (NTB, SKL, CLA and JCO), Merit Award from the US Department of Veterans Affairs (HJB), Lupus Research Institute (NTB), the Arthritis National Research Foundation Eng Tan Scholar Award (NTB), and the Lupus Foundation of Minnesota (NTB and SKL), Mayo Clinic Foundation (NTB), Kirkland Scholar Award (CLA) and the Wake Forest University Health Sciences Center for Public Health Genomics (LCD). We also thank the Instituto de Salud Carlos III (PI12/02558), partly supported with FEDER funds from the EU and the RNP Network BIOLUPUS financed by the European Science Foundation. The funders had no role in the study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish or preparation of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on Genes and Immunity website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kariuki, S., Ghodke-Puranik, Y., Dorschner, J. et al. Genetic analysis of the pathogenic molecular sub-phenotype interferon-alpha identifies multiple novel loci involved in systemic lupus erythematosus. Genes Immun 16, 15–23 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/gene.2014.57
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/gene.2014.57
This article is cited by
-
Germline genetic variation and predicting immune checkpoint inhibitor induced toxicity
npj Genomic Medicine (2022)
-
Backbone 1H, 15N, and 13C resonance assignments of the Phafin2 pleckstrin homology domain
Biomolecular NMR Assignments (2022)
-
Decreased sleep quality in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: a meta-analysis
Clinical Rheumatology (2021)
-
A Case with Purine Nucleoside Phosphorylase Deficiency Suffering from Late-Onset Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Lymphoma
Journal of Clinical Immunology (2020)
-
First trimester combined screening in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: impact of pre-analytical variables on risk assessment
Clinical Rheumatology (2019)