Abstract
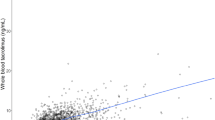
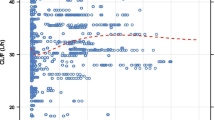
Cyclosporin (CyA) exhibits saturable binding to erythrocytes. A one-site binding model was fitted to data from renal transplant patients receiving CyA therapy. The average maximum binding capacity is 2560 µg CyA/liter of packed erythrocytes; the unbound CyA concentration associated with 50% saturation of the binding site is 67 µg/liter. Analysis indicates that whole-blood CyA measurement to monitor drug therapy should be viewed cautiously, particularly when the hematocrit varies considerably. The error in estimating absolute bioavailability at steady state from whole-blood measurements, resulting as a consequence of the saturable binding, has been explored. Although extrapolation to the therapeutic situation, which involves transient drug administration, is difficult, errors of up to 25% are anticipated. When an accurate estimate of bioavailability is required, analysis based on plasma data is proposed. For bioequivalence testing, both blood and plasma CyA data are equally acceptable.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
J. F. Borel. In D. J. G. White (ed.), Cyclosporin A—Proceedings of an International Conference on Cyclosporin A, Cambridge, Sept. 1981, Elsevier, Amsterdam, 1982, pp. 5–17.
W. Neiderberger, M. Lemaire, G. Maurer, K. Nussbaumer, and O. Wagner. Transplant Proc. 15 (Suppl. 1):2419–2421, (1983).
B. Legg and M. Rowland. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 39:599–603 (1987).
M. Lemaire and J. P. Tillement. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 34:715–718 (1982).
W. M. Awni and R. J. Sawchuk. Drug Metab. Disp. 13:133–138.
S. G. Carruthers, D. J. Freeman, J. C. Koegler, W. Howson, P. A. Keown, A. Laupacis, and C. R. Stiller. Clin. Chem. 29:180–183 (1983).
R. P. Agarwal, R. A. McPherson, and G. A. Threatte. Transplantation 42:627–632 (1986).
F. Follath, M. Wenk, S. Vozeh, G. Thiel, F. Brunner, R. Loertscher, M. Lemaire, K. Nussbaumer, W. Niederberger, and A. Wood. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 34:638–643 (1983).
G. Bandini, P. Ricci, G. Visani, S. Tura, and S. Boschi. Lancet 1 (No. 8327):762 (1983).
M. J. Bennett, K. H. Carpenter, E. Worthy, and J. S. Lilleyman. Clin. Chem. 30:817 (1984).
S. M. Faynor, T. P. Moyer, S. Sterioff, and M. W. McDonald. Mayo Clin. Proc. 59:571–572 (1984).
B. D. Kahan. Transplantation 40:457–476 (1985).
C. A. Wideman. Transplant Proc. 15(Suppl. 2):3168–3175 (1983).
R. J. Ptachcinski, R. Venkataramanan, and G. L. Burckart. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 11:107–132 (1986).
R. Donatsch, E. Abisch, M. Homberger, R. Traber, M. Trapp, and R. Voges. J. Immunoassay 2:19–32 (1981).
G. Maurer, H. R. Loosli, E. Schreier, and B. Keller. Drug Metab. Disp. 12:120–126 (1984).
S. E. Bradley, F. J. Inglefinger, G. P. Bradley, and J. J. Curry. J. Clin. Invest. 24:890–897 (1945).
S. Aziz, R. E. Oyer, and R. E. Kates. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 26:652–657 (1986).
A. Lindberg, B. Odlind, G. Tufveson, B. Lindström, and J. Gabrielsson. Transplant Proc. 18(Suppl. 5):144–152 (1986).
M. Rowland, L. Z. Benet, and G. G. Graham. J. Pharmacokinet. Biopharm. 1:123–136 (1973).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Legg, B., Rowland, M. Saturable Binding of Cyclosporin A to Erythrocytes: Estimation of Binding Parameters in Renal Transplant Patients and Implications for Bioavailability Assessment. Pharm Res 5, 80–85 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015932032609
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015932032609