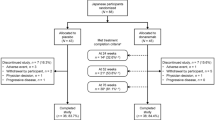
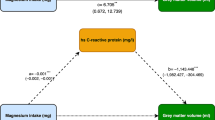
Abstract
There is evidence that activated immune-inflammatory and oxidative and nitrosative stress (IO&NS) pathways play a role in the pathophysiology of multiple sclerosis (MS) and depression. This study examines serum levels of interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-4, IL-6, and IL-10; peroxides (LOOH); nitric oxide metabolites (NOx); albumin; ferritin; C-reactive protein (CRP); and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-β NcoI polymorphism (rs909253) and gadolinium-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan in MS patients with (n = 42) and without (n = 108) depression and normal controls (n = 249). Depression is scored using the depressive subscale of the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS). The extent of neurological disability is measured using the Expanded Disability Status Scale (EDSS) at the same time of the abovementioned measurements and 5 years earlier. Disease progression is assessed as actual EDSS—EDSS 5 years earlier. Three variables discriminate MS patients with depression from those without depression, i.e., increased IL-6 and lower IL-4 and albumin. Binary logistic regression showed that MS with depression (versus no depression) was characterized by more gastrointestinal symptoms and disease progression, higher serum IL-6, and lower albumin levels. In subjects with MS, the HADS score was significantly predicted by three EDSS symptoms, i.e., pyramidal, gastrointestinal, and visual symptoms. Fifty-eight percent of the variance in the HADS score was predicted by gastrointestinal symptoms, visual symptoms, the TNFB1/B2 genotype, and contrast enhancement (both inversely associated). There were no significant associations between depression in MS and type of MS, duration of illness, age, sex, nicotine dependence, and body mass index. MS with depression is associated with signs of peripheral inflammation, more disability, disease progression, gastrointestinal and visual symptoms, but less contrast enhancement as compared to MS without depression. It is concluded that depression is part of the neurological symptoms of MS and that its expression is primed by peripheral inflammation while acute neuroinflammation and the TNFB1/B2 genotype may be protective.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gironi M, Borgiani B, Mariani E, Cursano C, Mendozzi L, Cavarretta R, Saresella M, Clerici M et al (2014) Oxidative stress is differentially present in multiple sclerosis courses, early evident, and unrelated to treatment. J Immunol Res 2014:961863
Miller E, Walczak A, Saluk J, Ponczek MB, Majsterek I (2012) Oxidative modification of patient’s plasma proteins and its role in pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis. Clin Biochem 45:26–30
Gonsette RE (2008) Neurodegeneration in multiple sclerosis: the role of oxidative stress and excitotoxicity. J Neurol Sci 274:48–53
Ortiz GG, Pacheco-Moisés FP, Bitzer-Quintero OK, Ramírez-Anguiano AC, Flores-Alvarado LJ, Ramírez-Ramírez V, Macias-Islas MA, Torres-Sánchez ED (2013) Immunology and oxidative stress in multiple sclerosis: clinical and basic approach. Clin Dev Immunol 2013:708659
Morris G, Maes M (2013) Myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome and encephalomyelitis disseminata/multiple sclerosis show remarkable levels of similarity in phenomenology and neuroimmune characteristics. BMC Med 11:205
Dujmovic I, Mangano K, Pekmezovic T, Quattrocchi C, Mesaros S, Stojsavljevic N, Nicoletti F, Drulovic J (2009) The analysis of IL-1 beta and its naturally occurring inhibitors in multiple sclerosis: the elevation of IL-1 receptor antagonist and IL-1 receptor type II after steroid therapy. J Neuroimmunol 207:101–106
Argaw AT, Zhang Y, Snyder BJ, Zhao ML, Kopp N, Lee SC, Raine CS, Brosnan CF et al (2006) IL-1beta regulates blood–brain barrier permeability via reactivation of the hypoxia-angiogenesis program. J Immunol 177:5574–5584
Hauser SL, Doolittle TH, Lincoln R, Brown RH, Dinarello CA (1990) Cytokine accumulations in CSF of multiple sclerosis patients: frequent detection of interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor but not interleukin-6. Neurology 40:1735–1739
Sharief MK, Hentges R (1991) Association between tumor necrosis factor-alpha and disease progression in patients with multiple sclerosis. N Engl J Med 325:467–472
Al-Omaishi J, Bashir R, Gendelman HE (1999) The cellular immunology of multiple sclerosis. J Leukoc Biol 65:444–452
Frei K, Fredrikson S, Fontana A (1991) Link H: interleukin-6 is elevated in plasma in multiple sclerosis. J Neuroimmunol 31:147–153
Kurtzke JF (1983) Rating neurologic impairment in multiple sclerosis: an expanded disability status scale (EDSS). Neurology 33(11):1444–1452
Oliveira SR, Kallaur AP, Simão AN, Morimoto HK, Lopes J, Panis C, Petenucci DL, da Silva E et al (2012) Oxidative stress in multiple sclerosis patients in clinical remission: association with the expanded disability status scale. J Neurol Sci 321:49–53
Ljubisavljevic S, Stojanovic I, Cvetkovic T, Vojinovic S, Stojanov D, Stojanovic D, Stefanovic N, Pavlovic D (2014) Erythrocytes’ antioxidative capacity as a potential marker of oxidative stress intensity in neuroinflammation. J Neurol Sci 337:8–13
Gajewski TF, Schell SR, Nau G, Fitch FW (1989) Regulation of T-cell activation: differences among T-cell subsets. Immunol Rev 111:79–110
Murphy KM, Reiner SL (2002) The lineage decisions of helper T cells. Nat Rev Immunol 2:933–944
Imam SA, Guyton MK, Haque A, Vandenbark A, Tyor WR, Ray SK, Banik NL (2007) Increased calpain correlates with Th1 cytokine profile in PBMCs from MS patients. J Neuroimmunol 190:139–145
Koguchi K, Anderson DE, Yang L, O’Connor KC, Kuchroo VK, Hafler DA (2006) Dysregulated T cell expression of TIM3 in multiple sclerosis. J Exp Med 203:1413–1418
Rodriguez-Sainz Mdel C, Sanchez-Ramon S, de Andres C, Rodriguez-Mahou M, Munoz-Fernandez MA (2002) Th1/Th2 cytokine balance and nitric oxide in cerebrospinal fluid and serum from patients with multiple sclerosis. Eur Cytokine Netw 13:110–114
Kallaur AP, Oliveira SR, Simão AN, de Almeida ER, Morimoto HK, Alfieri DF, Pereira WL, Borelli SD et al (2014) Tumor necrosis factor beta NcoI polymorphism is associated with inflammatory and metabolic markers in multiple sclerosis patients. J Neurol Sci 346:156–163
Fiorini A, Koudriavtseva T, Bucaj E, Coccia R, Foppoli C, Giorgi A, Schininà ME, Di Domenico F et al (2013) Involvement of oxidative stress in occurrence of relapses in multiple sclerosis: the spectrum of oxidatively modified serum proteins detected by proteomics and redox proteomics analysis. PLoS One 8:e65184
Encinas JM, Manganas L, Enikolopov G (2005) Nitric oxide and multiple sclerosis. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep 5:232–238
Skokou M, Soubasi E, Gourzis P (2012) Depression in multiple sclerosis: a review of assessment and treatment approaches in adult and pediatric populations. ISRN Neurol 2012:427102
Feinstein A, Magalhaes S, Richard JF, Audet B, Moore C (2014) The link between multiple sclerosis and depression. Nat Rev Neurol 10(9):507–517
Maes M, Kubera M, Obuchowiczwa E, Goehler L, Brzeszcz J (2011) Depression’s multiple comorbidities explained by (neuro)inflammatory and oxidative & nitrosative stress pathways. Neuro Endocrinol Lett 32:7–24
Vattakatuchery JJ, Rickards H, Cavanna AE (2011) Pathogenic mechanisms of depression in multiple sclerosis. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci 23:261–276
Fragoso YD, Frota ER, Lopes JS, Noal JS, Giacomo MC, Gomes S, Gonçalves MV, da Gama PD et al (2010) Severe depression, suicide attempts, and ideation during the use of interferon beta by patients with multiple sclerosis. Clin Neuropharmacol 33(6):312–316
Ziemssen T, Bajenaru OA, Carrá A, de Klippel N, de Sá JC, Edland A, Frederiksen JL, Heinzlef O et al (2014) A 2-year observational study of patients with relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis converting to glatiramer acetate from other disease-modifying therapies: the COPTIMIZE trial. J Neurol 261:2101–2111
Zigmond AS, Snaith P (1983) The hospital anxiety and depression scale. Acta Psychiatr Scand 67:361–370
Norton S, Cosco T, Doyle F, Done J, Sacker A (2013) The Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale: a meta confirmatory factor analysis. J Psychosom Res 74:74–81
Maes M, Galecki P, Chang YS, Berk M (2011) A review on the oxidative and nitrosative stress (O&NS) pathways in major depression and their possible contribution to the (neuro)degenerative processes in that illness. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 35:676–692
Kahl KG, Kruse N, Faller H, Weiss H, Rieckmann P (2002) Expression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interferon-gamma mRNA in blood cells correlates with depression scores during an acute attack in patients with multiple sclerosis. Psychoneuroendocrinology 27:671–681
Pokryszko-Dragan A, Frydecka I, Kosmaczewska A, Ciszak L, Bilinska M, Gruszka E, Podemski R, Frydecka D (2012) Stimulated peripheral production of interferon-gamma is related to fatigue and depression in multiple sclerosis. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 114:1153–1158
Mohr DC, Goodkin DE, Islar J, Hauser SL, Genain CP (2001) Treatment of depression is associated with suppression of nonspecific and antigen-specific T(H)1 responses in multiple sclerosis. Arch Neurol 58:1081–1086
Polman CH, Reingold SC, Edan G, Filippi M, Hartung HP, Kappos L, Lublin FD, Metz LM et al (2005) Diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis: 2005 revisions to the “McDonald criteria”. Ann Neurol 58:840–846
Polman CH, Reingold SC, Banwell B, Clanet M, Cohen JA, Filippi M, Fujihara K, Havrdova E et al (2011) Diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis: 2010 revisions to the McDonald criteria. Ann Neurol 69:292–302
Lublin FD, Reingold SC (1996) Defining the clinical course of multiple sclerosis: results of an international survey. National Multiple Sclerosis Society (USA) Advisory Committee on Clinical Trials of New Agents in Multiple Sclerosis. Neurology 46:907–911
Honarmand K, Feinstein A (2009) Validation of the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale for use with multiple sclerosis patients. Mult Scler 15:1518–1524
Navarro-Gonzálvez JA, García-Benayas C, Arenas J (1998) Semiautomated measurement of nitrate in biological fluids. Clin Chem 44:679–681
Gonzalez Flecha B, Llesuy S, Boveris A (1991) Hydroperoxide-initiated chemiluminescence: an assay for oxidative stress in biopsies of heart, liver, and muscle. Free Radic Biol Med 10:93–100
Repetto M, Reides C, Carretero MLG, Costa M, Griemberg G, Llesuy S (1996) Oxidative stress in blood of HIV infected patients. Clin Chim Acta 255:107–117
Majetschak M, Flohé S, Obertacke U, Schröder J, Staubach K, Nast-Kolb D, Schade FU, Stüber F (1999) Relation of a TNF gene polymorphism to severe sepsis in trauma patients. Ann Surg 230:207–214
Majetschak M, Obertacke U, Schade FU, Bardenheuer M, Voggenreiter G, Bloemeke B, Heesen M (2002) Tumor necrosis factor gene polymorphisms, leukocyte function, and sepsis susceptibility in blunt trauma patients. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol 9:1205–1211
Delongui F, Carvalho Grion CM, Ehara Watanabe MA, Morimoto HK, Bonametti AM, Maeda Oda JM, Kallaur AP, Matsuo T et al (2011) Association of tumor necrosis factor β genetic polymorphism and sepsis susceptibility. Exp Ther Med 2(2):349–356
Maes M, Vandewoude M, Scharpé S, De Clercq L, Stevens W, Lepoutre L, Schotte C (1991) Anthropometric and biochemical assessment of the nutritional state in depression: evidence for lower visceral protein plasma levels in depression. J Affect Disord 23:25–33
Maes M (1993) A review on the acute phase response in major depression. Rev Neurosci 4:407–416
Liu Y, Ho RC, Mak A (2012) Interleukin (IL)-6, tumour necrosis factor alpha (TNF-a) and soluble interleukin-2 receptors (sIL-2R) are elevated in patients with major depressive disorder: a meta-analysis and meta-regression. J Affect Disord 139(3):230–239
Valkanova V, Ebmeier KP, Allan CL (2013) CRP, IL-6 and depression: a systematic review and meta-analysis of longitudinal studies. J Affect Disord 150:736–744
Koutsouraki E, Hatzifilipou E, Michmizos D, Cotsavasiloglou C, Costa V, Baloyannis S (2011) Increase in interleukin-6 levels is related to depressive phenomena in the acute (relapsing) phase of multiple sclerosis. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci 23(4):442–448
Scheller J, Chalaris A, Schmidt-Arras D, Rose-John S (2011) The pro- and anti-inflammatory properties of the cytokine interleukin-6. Biochim Biophys Acta 1813:878–888
Maes M, Anderson G, Kubera M, Berk M (2014) Targeting classical IL-6 signalling or IL-6 trans-signalling in depression? Expert Opin Ther Targets 18:495–512
Bakshi R, Czarnecki D, Shaikh ZA, Priore RL, Janardhan V, Kaliszky Z, Kinkel PR (2000) Brain MRI lesions and atrophy are related to depression in multiple sclerosis. Neuroreport 11:1153–1158
Rovira A, Auger C, Alonso J (2013) Magnetic resonance monitoring of lesion evolution in multiple sclerosis. Ther Adv Neurol Disord 6(5):298–310
Cotton F, Weiner HL, Jolesz FA, Guttmann CR (2003) MRI contrast uptake in new lesions in relapsing-remitting MS followed at weekly intervals. Neurology 60(4):640–646
Filippi M, Agosta F, Spinelli EG, Rocca MA (2013) Imaging resting state brain function in multiple sclerosis. J Neurol 260:1709–1713
Meier DS, Guttmann CR (2003) Time-series analysis of MRI intensity patterns in multiple sclerosis. Neuroimage 20:1193–1209
Meier DS, Weiner HL, Guttmann CR (2007) MR imaging intensity modeling of damage and repair in multiple sclerosis: relationship of short-term lesion recovery to progression and disability. Am J Neuroradiol 28:1956–1963
Najjar S, Pearlman DM, Devinsky O, Najjar A, Zagzag D (2013) Neurovascular unit dysfunction with blood–brain barrier hyperpermeability contributes to major depressive disorder: a review of clinical and experimental evidence. J Neuroinflammation 10:142
Koch MW, Patten S, Berzins S, Zhornitsky S, Greenfield J, Wall W, Metz LM (2015) Depression in multiple sclerosis: a long-term longitudinal study. Mult Scler 21:76–82
Alajbegovic A, Loga N, Tiro N, Alajbegovic S, Cindro V, Hozo I (2009) Cognitive and depressive disorders in multiple sclerosis. Acta Clin Croat 48:3–8
Koch M, Mostert J, Heerings M, Uyttenboogaart M, De Keyser J (2009) Fatigue, depression and disability accumulation in multiple sclerosis: a cross-sectional study. Eur J Neurol 16:348–352
Askari F, Ghajarzadeh M, Mohammadifar M, Azimi A, Sahraian MA, Owji M (2014) Anxiety in patients with multiple sclerosis: association with disability, depression, disease type and sex. Acta Med Iran 52:889–892
Gay MC, Vrignaud P, Garitte C, Meunier C (2010) Predictors of depression in multiple sclerosis patients. Acta Neurol Scand 2010:161–170
Finkelsztejn A, Cristovam Rdo A, Moraes GS, Lopes MG, Silva AV, Garcia MS, Cola CM, Bastiani CE et al (2009) Clinical features of multiple sclerosis in the south of Brazil: a partial analysis. Arq Neuropsiquiatr 67:1071–1075
Mattioli F, Bellomi F, Stampatori C, Parrinello G, Capra R (2011) Depression, disability and cognitive impairment in multiple sclerosis: a cross sectional Italian study. Neurol Sci 32:825–832
Mendes MF, Tilbery CP, Balsimelli S, Moreira MA, Barão-Cruz AM (2003) Depression in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. Arq Neuropsiquiatr 61:591–595
Shen Y, Bai L, Gao Y, Cui F, Tan Z, Tao Y, Sun C, Zhou L (2014) Depressive symptoms in multiple sclerosis from an in vivo study with TBSS. Biomed Res Int 2014:148465
Tsivgoulis G, Triantafyllou N, Papageorgiou C, Evangelopoulos ME, Kararizou E, Sfagos C, Vassilopoulos D (2007) Associations of the Expanded Disability Status Scale with anxiety and depression in multiple sclerosis outpatients. Acta Neurol Scand 115:67–72
Ayatollahi P, Nafissi S, Eshraghian MR, Kaviani H, Tarazi A (2007) Impact of depression and disability on quality of life in Iranian patients with multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler 13:275–277
Chwastiak LA, Ehde DM (2007) Psychiatric issues in multiple sclerosis. Psychiatr Clin N Am 30:803–817
Lobentanz IS, Asenbaum S, Vass K, Sauter C, Klösch G, Kollegger H, Kristoferitsch W, Zeitlhofer J (2004) Factors influencing quality of life in multiple sclerosis patients: disability, depressive mood, fatigue and sleep quality. Acta Neurol Scand 110:6–13
Zephir H, De Seze J, Stojkovic T, Delisse B, Ferriby D, Cabaret M, Vermersch P (2003) Multiple sclerosis and depression: influence of interferon beta therapy. Mult Scler 9:284–288
Levinthal DJ, Rahman A, Nusrat S, O’Leary M, Heyman R, Bielefeldt K (2013) Adding to the burden: gastrointestinal symptoms and syndromes in multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler Int 2013:319201
Maes M, Kubera M, Leunis JC (2008) The gut-brain barrier in major depression: intestinal mucosal dysfunction with an increased translocation of LPS from gram negative enterobacteria (leaky gut) plays a role in the inflammatory pathophysiology of depression. Neuro Endocrinol Lett 29:117–124
Geffard M, Bodet D, Martinet Y, Dabadie MP (2002) Intérêt de l’évaluationd’IgM et d’IgA spécifiques circulant dans le sérum de malades atteints de sclérose en plaques (SEP). Immuno Anal Biol Spéc 17:302–310
Geffard M, Duleu S, Bessede A, Covenas R, Mangas A (2011) A new paradigm for multiple sclerosis. In: Geffard M (ed) Multiple sclerosis. A new paradigm. Nova Science Publishers 153–84
Bodet D, Glaize G, Dabadie MP, Geffard M (2004) Suivi immunobiologique de malades atteints de Sclérose en Plaques. Immuno Anal Biol Spéc 19:138–147
Acknowledgments
This study is supported by the Health Sciences Postgraduate Program at the State University of Londrina, Brazil; the Ministry for Sciences and Technology of Brazil (CNPq); and the Brazilian Federal Agency for Support and Evaluation of Graduate Education (CAPES). MM is supported by a special CNPq (National Council of Scientific and Technology), PVE fellowship, and the Health Sciences Postgraduate Program fellowship, Londrina State University (UEL).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors’ Contributions
All authors contributed equally to this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kallaur, A.P., Lopes, J., Oliveira, S.R. et al. Immune-Inflammatory and Oxidative and Nitrosative Stress Biomarkers of Depression Symptoms in Subjects with Multiple Sclerosis: Increased Peripheral Inflammation but Less Acute Neuroinflammation. Mol Neurobiol 53, 5191–5202 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-015-9443-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-015-9443-4