Abstract
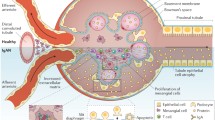
IgA nephropathy (IgAN) is the most common glomerulonephritis in the world. The hallmark of IgAN is underglycosylation in the hinge region of IgA1. Increasing evidence supports the underglycosylated IgA-containing immune-complex including IgG antibodies against the glycans of the hinge region of IgA1 are key factors for mesangial deposition and then trigger inflammation and glomerular injury. The polymeric IgA is produced after aberrant mucosal IgA response. The displacement of mucosal B cells to systemic lymphoid organs and bone marrow may arise from abnormal trafficking of lymphocytes along the mucosa–bone marrow axis involving changes of chemokines and adhesion molecules. This review will summarize the works on the genetics, the mucosal and systemic IgA immune response, mechanism of underglycosylation of IgA1, and the pathological effect of mesangial IgA deposition in IgAN.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berger J, Hinglas N (1968) Les depots intercapillaries d’IgA-IgG (Intercapillary deposits of IgA-IgG). J Urol Nephrol (Paris) 74:694–695
Glassock RJ (2008) IgA nephropathy: challenges and opportunities. Cleve Clin J Med 75:569–576
Rai A, Nast C, Adler S (1999) Henoch-Schonlein purpura nephritis. J Am Soc Nephrol 10:2637–2644
Donadio JV, Grande JP (2002) IgA nephropathy. N Engl J Med 347:738–748
D’Amico G, Imbasciati E, Barbiano Di Belgioioso G et al (1985) Idiopathic IgA mesangial nephropathy. Clinical and histological study of 374 patients. Medicine (Baltimore) 64:49–60
Berger J (1988) Recurrence of IgA nephropathy in renal allografts. Am J Kidney Dis 12:371–372
Gharavi AG, Yan Y, Scolari F et al (2000) IgA nephropathy, the most common cause of glomerulonephritis, is linked to 6q22-23. Nat Genet 26:354–357
Bisceglia L, Cerullo G, Forabosco P et al (2006) Genetic heterogeneity in Italian families with IgA nephropathy: suggestive linkage for two novel IgA nephropathy loci. Am J Hum Genet 79:1130–1134
Schena FP, Cerullo G, Torres DD et al (2007) Searching for IgA nephropathy candidate genes: genetic studies combined with high throughput innovative investigations. Contrib Nephrol 157:80–89
Akira S, Uematsu S, Takeuchi O (2006) Pathogen recognition and innate immunity. Cell 124:783–801
Suzuki H, Suzuki Y, Narita I et al (2008) Toll-like receptor 9 affects severity of IgA nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol 19:2384–2395
Yoon HJ, Shin JH, Yang SH et al (2003) Association of the CD14 gene −159 C polymorphism with progression of IgA nephropathy. J Med Genet 40:104–108
Narita I, Goto S, Saito N et al (2001) Genetic polymorphisms in the promoter and 5′ UTR region of the Fc alpha receptor (CD89) are not associated with a risk of IgA nephropathy. J Hum Genet 46:694–698
Tsuge T, Shimokawa T, Horikoshi S, Tomino Y, Ra C (2001) Polymorphism in promoter region of Fcalpha receptor gene in patients with IgA nephropathy. Hum Genet 108:128–133
Vuong MT, Hahn-Zoric M, Lundberg S et al (2010) Association of soluble CD89 levels with disease progression but not susceptibility in IgA nephropathy. Kidney Int (in press)
Suzuki H, Fan R, Zhang Z et al (2009) Aberrantly glycosylated IgA1 in IgA nephropathy patients is recognized by IgG antibodies with restricted heterogeneity. J Clin Invest 119:1668–1677
Tanaka Y, Suzuki Y, Tsuge T et al (2005) FcgammaRIIa-131R allele and FcgammaRIIIa-176V/V genotype are risk factors for progression of IgA nephropathy. Nephrol Dial Transplant 20:2439–2445
Xu G, He Q, Shou Z et al (2007) NA1/NA2 heterozygote of Fcgr3b is a risk factor for progression of IgA nephropathy in Chinese. J Clin Lab Anal 21:298–302
Anders HJ, Vielhauer V, Schlondorff D (2003) Chemokines and chemokine receptors are involved in the resolution or progression of renal disease. Kidney Int 63:401–415
Michael NL, Louie LG, Rohrbaugh AL et al (1997) The role of CCR5 and CCR2 polymorphisms in HIV-1 transmission and disease progression. Nat Med 3:1160–1162
Berthoux FC, Berthoux P, Mariat C, Thibaudin L, Afiani A, Linossier MT (2006) CC-chemokine receptor five gene polymorphism in primary IgA nephropathy: the 32 bp deletion allele is associated with late progression to end-stage renal failure with dialysis. Kidney Int 69:565–572
Panzer U, Schneider A, Steinmetz OM et al (2005) The chemokine receptor 5 Delta32 mutation is associated with increased renal survival in patients with IgA nephropathy. Kidney Int 67:75–81
Springer TA (1994) Traffic signals for lymphocyte recirculation and leukocyte emigration: the multistep paradigm. Cell 76:301–314
Takaeda M, Yokoyama H, Segawa-Takaeda C, Wada T, Kobayashi K (2002) High endothelial venule-like vessels in the interstitial lesions of human glomerulonephritis. Am J Nephrol 22:48–57
Suzuki Y, Tomino Y (2007) The mucosa-bone-marrow axis in IgA nephropathy. Contrib Nephrol 157:70–79
Takei T, Iida A, Nitta K et al (2002) Association between single-nucleotide polymorphisms in selectin genes and immunoglobulin A nephropathy. Am J Hum Genet 70:781–786
Watanabe Y, Inoue T, Okada H et al (2006) Impact of selectin gene polymorphisms on rapid progression to end-stage renal disease in patients with IgA nephropathy. Intern Med 45:947–951
Suzuki H, Suzuki Y, Yamanaka T et al (2005) Genome-wide scan in a novel IgA nephropathy model identifies a susceptibility locus on murine chromosome 10, in a region syntenic to human IGAN1 on chromosome 6q22-23. J Am Soc Nephrol 16:1289–1299
Feehally J, Farrall M, Boland A et al (2010) HLA has strongest association with IgA nephropathy in genome-wide analysis. J Am Soc Nephrol 21:1791–1797
Ebihara I, Hirayama K, Yamamoto S, Muro K, Yamagata K, Koyama A (2001) Th2 predominance at the single-cell level in patients with IgA nephropathy. Nephrol Dial Transplant 16:1783–1789
de Caestecker MP, Bottomley M, Telfer BA, Hutchinson IV, Vose BM, Ballardie FW (1993) Detection of abnormal peripheral blood mononuclear cell cytokine networks in human IgA nephropathy. Kidney Int 44:1298–1308
Yano N, Endoh M, Nomoto Y, Sakai H, Fadden K, Rifai A (1997) Phenotypic characterization of cytokine expression in patients with IgA nephropathy. J Clin Immunol 17:396–403
Bantis C, Heering PJ, Aker S, Klein-Vehne N, Grabensee B, Ivens K (2004) Association of interleukin-10 gene G-1082A polymorphism with the progression of primary glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int 66:288–294
Bantis C, Heering PJ, Aker S, Schwandt C, Grabensee B, Ivens K (2008) Influence of interleukin-10 gene G-1082A polymorphism on recurrent IgA nephropathy. J Nephrol 21:941–946
Chin HJ, Na KY, Kim SJ et al (2005) Interleukin-10 promoter polymorphism is associated with the predisposition to the development of IgA nephropathy and focal segmental glomerulosclerosis in Korea. J Korean Med Sci 20:989–993
Lim CS, Kim YS, Chae DW et al (2005) Association of C-509T and T869C polymorphisms of transforming growth factor-beta1 gene with susceptibility to and progression of IgA nephropathy. Clin Nephrol 63:61–67
Schena FP, Cerullo G, Torres DD et al (2006) Role of interferon-gamma gene polymorphisms in susceptibility to IgA nephropathy: a family-based association study. Eur J Hum Genet 14:488–496
Obara W, Iida A, Suzuki Y et al (2003) Association of single-nucleotide polymorphisms in the polymeric immunoglobulin receptor gene with immunoglobulin A nephropathy (IgAN) in Japanese patients. J Hum Genet 48:293–299
Shimada S, Kawaguchi-Miyashita M, Kushiro A et al (1999) Generation of polymeric immunoglobulin receptor-deficient mouse with marked reduction of secretory IgA. J Immunol 163:5367–5373
Ohtsubo S, Iida A, Nitta K et al (2005) Association of a single-nucleotide polymorphism in the immunoglobulin mu-binding protein 2 gene with immunoglobulin A nephropathy. J Hum Genet 50:30–35
Lou T, Zhang J, Gale DP et al (2010) Variation in IGHMBP2 is not associated with IgA nephropathy in independent studies of UK Caucasian and Chinese Han patients. Nephrol Dial Transplant 25:1547–1554
Li GS, Zhang H, Lv JC, Shen Y, Wang HY (2007) Variants of C1GALT1 gene are associated with the genetic susceptibility to IgA nephropathy. Kidney Int 71:448–453
Narita I, Kaneko Y, Kondo D, Goto S, Sakatsume M, Gejyo F (2007) The genetic susceptibility to IgA nephropathy: a novel functional candidate gene for incomplete O-glycosylation of IgA1. Kidney Int 71:379–381
Pirulli D, Crovella S, Ulivi S et al (2009) Genetic variant of C1GalT1 contributes to the susceptibility to IgA nephropathy. J Nephrol 22:152–159
Zhu L, Tang W, Li G et al (2009) Interaction between variants of two glycosyltransferase genes in IgA nephropathy. Kidney Int 76:190–198
Li GS, Zhu L, Zhang H et al (2007) Variants of the ST6GALNAC2 promoter influence transcriptional activity and contribute to genetic susceptibility to IgA nephropathy. Hum Mutat 28:950–957
Zheng F, Kundu GC, Zhang Z, Ward J, DeMayo F, Mukherjee AB (1999) Uteroglobin is essential in preventing immunoglobulin A nephropathy in mice. Nat Med 5:1018–1025
Kim YS, Kang D, Kwon DY et al (2001) Uteroglobin gene polymorphisms affect the progression of immunoglobulin A nephropathy by modulating the level of uteroglobin expression. Pharmacogenetics 11:299–305
Matsunaga A, Numakura C, Kawakami T et al (2002) Association of the uteroglobin gene polymorphism with IgA nephropathy. Am J Kidney Dis 39:36–41
Narita I, Saito N, Goto S et al (2002) Role of uteroglobin G38A polymorphism in the progression of IgA nephropathy in Japanese patients. Kidney Int 61:1853–1858
Szelestei T, Bahring S, Kovacs T et al (2000) Association of a uteroglobin polymorphism with rate of progression in patients with IgA nephropathy. Am J Kidney Dis 36:468–473
Yong D, QingQing W, Hua L et al (2006) Association of uteroglobin G38A polymorphism with IgA nephropathy: a meta-analysis. Am J Kidney Dis 48:1–7
Miyata T, Nangaku M, Suzuki D et al (1998) A mesangium-predominant gene, megsin, is a new serpin upregulated in IgA nephropathy. J Clin Invest 102:828–836
Suzuki D, Miyata T, Nangaku M et al (1999) Expression of megsin mRNA, a novel mesangium-predominant gene, in the renal tissues of various glomerular diseases. J Am Soc Nephrol 10:2606–2613
Li YJ, Du Y, Li CX et al (2004) Family-based association study showing that immunoglobulin A nephropathy is associated with the polymorphisms 2093 C and 2180 T in the 3′ untranslated region of the Megsin gene. J Am Soc Nephrol 15:1739–1743
Lim CS, Kim SM, Oh YK et al (2008) Megsin 2093T-2180C haplotype at the 3′ untranslated region is associated with poor renal survival in Korean IgA nephropathy patients. Clin Nephrol 70:101–109
Maixnerova D, Merta M, Reiterova J et al (2008) The influence of two megsin polymorphisms on the progression of IgA nephropathy. Folia Biol (Praha) 54:40–45
Xia Y, Li Y, Du Y et al (2006) Association of MEGSIN 2093C-2180T haplotype at the 3′ untranslated region with disease severity and progression of IgA nephropathy. Nephrol Dial Transplant 21:1570–1574
Xia YF, Huang S, Li X et al (2006) A family-based association study of megsin A23167G polymorphism with susceptibility and progression of IgA nephropathy in a Chinese population. Clin Nephrol 65:153–159
Higuchi T, Orita T, Nakanishi S et al (2004) Molecular cloning, genomic structure, and expression analysis of MUC20, a novel mucin protein, up-regulated in injured kidney. J Biol Chem 279:1968–1979
Li G, Zhang H, Lv J, Hou P, Wang H (2006) Tandem repeats polymorphism of MUC20 is an independent factor for the progression of immunoglobulin A nephropathy. Am J Nephrol 26:43–49
Rigat B, Hubert C, Alhenc-Gelas F, Cambien F, Corvol P, Soubrier F (1990) An insertion/deletion polymorphism in the angiotensin I-converting enzyme gene accounting for half the variance of serum enzyme levels. J Clin Invest 86:1343–1346
Yong D, Qing WQ, Hua L et al (2006) Association of angiotensin I-converting enzyme gene insertion/deletion polymorphism and IgA nephropathy: a meta-analysis. Am J Nephrol 26:511–518
Woo KT, Lau YK, Zhao Y et al (2007) Disease progression, response to ACEI/ATRA therapy and influence of ACE gene in IgA nephritis. Cell Mol Immunol 4:227–232
Rodriguez-Perez JC, Macias-Reyes A, Jimenez-Sosa A et al (2009) A synergistic association of ACE I/D and eNOS G894T gene variants with the progression of immunoglobulin A nephropathy—a pilot study. Am J Nephrol 30:303–309
Pei Y, Scholey J, Thai K, Suzuki M, Cattran D (1997) Association of angiotensinogen gene T235 variant with progression of immunoglobin A nephropathy in Caucasian patients. J Clin Invest 100:814–820
Jeunemaitre X, Soubrier F, Kotelevtsev YV et al (1992) Molecular basis of human hypertension: role of angiotensinogen. Cell 71:169–180
Cox SN, Sallustio F, Serino G et al (2010) Altered modulation of WNT-beta-catenin and PI3K/Akt pathways in IgA nephropathy. Kidney Int 78:396–407
Iio K, Nagasawa Y, Iwatani H et al (2010) Microarray analysis of tonsils in immunoglobulin A nephropathy patients. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 393:565–570
Vonica A, Rosa A, Arduini B, Brivanlou AH (2010) APOBEC2, a selective inhibitor of TGFbeta signaling, regulates left-right axis specification during early embryogenesis. Dev Biol (in press)
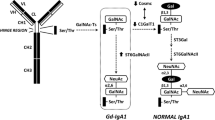
Narita I, Gejyo F (2008) Pathogenetic significance of aberrant glycosylation of IgA1 in IgA nephropathy. Clin Exp Nephrol 12:332–338
Brandtzaeg P, Johansen FE (2005) Mucosal B cells: phenotypic characteristics, transcriptional regulation, and homing properties. Immunol Rev 206:32–63
Tomino Y (2010) Spontaneous animal model, ddY mouse, for studying the pathogenesis and treatment in patients with immunoglobulin A nephropathy. Nephrology 15:1–6
Monteiro RC (2010) Role of IgA and IgA fc receptors in inflammation. J Clin Immunol 30:1–9
Galla JH (1995) IgA Nephropathy. Kidney Int 47:377–387
Conley ME, Cooper MD, Michael AF (1980) Selective deposition of immunoglobulin A1 in immunoglobulin A nephropathy, anaphylactoid purpura nephritis, and systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest 66:1432–1436
Suzuki H, Moldoveanu Z, Hall S et al (2008) IgA1-secreting cell lines from patients with IgA nephropathy produce aberrantly glycosylated IgA1. J Clin Invest 118:629–639
Mestecky J, Tomana M, Crowley-Nowick PA, Moldoveanu Z, Julian BA, Jackson S (1993) Defective galactosylation and clearance of IgA1 molecules as a possible etiopathogenic factor in IgA nephropathy. Contrib Nephrol 104:172–182
Hiki Y, Horii A, Iwase H et al (1995) O-linked oligosaccharide on IgA1 hinge region in IgA nephropathy. Fundamental study for precise structure and possible role. Contrib Nephrol 111:73–84
Allen AC, Harper SJ, Feehally J (1995) Galactosylation of N- and O-linked carbohydrate moieties of IgA1 and IgG in IgA nephropathy. Clin Exp Immunol 100:470–474
Kokubo T, Hiki Y, Iwase H et al (1998) Protective role of IgA1 glycans against IgA1 self-aggregation and adhesion to extracellular matrix proteins. J Am Soc Nephrol 9:2048–2054
Novak J, Tomana M, Matousovic K et al (2005) IgA1-containing immune complexes in IgA nephropathy differentially affect proliferation of mesangial cells. Kidney Int 67:504–513
Wang Y, Zhao MH, Zhang YK, Li XM, Wang HY (2004) Binding capacity and pathophysiological effects of IgA1 from patients with IgA nephropathy on human glomerular mesangial cells. Clin Exp Immunol 136:168–175
Monteiro RC, Moura IC, Launay P et al (2002) Pathogenic significance of IgA receptor interactions in IgA nephropathy. Trends Mol Med 8:464–468
Moldoveanu Z, Wyatt RJ, Lee JY et al (2007) Patients with IgA nephropathy have increased serum galactose-deficient IgA1 levels. Kidney Int 71:1148–1154
Ju T, Brewer K, D’Souza A, Cummings RD, Canfield WM (2002) Cloning and expression of human core 1 beta1, 3-galactosyltransferase. J Biol Chem 277:178–186
Iwasaki H, Zhang Y, Tachibana K et al (2003) Initiation of O-glycan synthesis in IgA1 hinge region is determined by a single enzyme, UDP-N-acetyl-alpha-D-galactosamine:polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase 2. J Biol Chem 278:5613–5621
Qin W, Zhou Q, Yang LC et al (2005) Peripheral B lymphocyte beta1, 3-galactosyltransferase and chaperone expression in immunoglobulin A nephropathy. J Intern Med 258:467–477
Chintalacharuvu SR, Nagy NU, Sigmund N, Nedrud JG, Amm ME, Emancipator SN (2001) T cell cytokines determine the severity of experimental IgA nephropathy by regulating IgA glycosylation. Clin Exp Immunol 126:326–333
Yamada K, Kobayashi N, Ikeda T et al (2010) Down-regulation of core 1 {beta}1, 3-galactosyltransferase and Cosmc by Th2 cytokine alters O-glycosylation of IgA1. Nephrol Dial Transplant 25:3890–3897
Qin W, Zhong X, Fan JM, Zhang YJ, Liu XR, Ma XY (2008) External suppression causes the low expression of the Cosmc gene in IgA nephropathy. Nephrol Dial Transplant 23:1608–1614
Smith AC, de Wolff JF, Molyneux K, Feehally J, Barratt J (2006) O-glycosylation of serum IgD in IgA nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol 17:1192–1199
Xie Y, Chen X, Nishi S, Narita I, Gejyo F (2004) Relationship between tonsils and IgA nephropathy as well as indications of tonsillectomy. Kidney Int 65:1135–1144
Kiyono H, Fukuyama S (2004) NALT- versus Peyer’s-patch-mediated mucosal immunity. Nat Rev Immunol 4:699–710
Brandtzaeg P (2010) Function of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue in antibody formation. Immunol Invest 39:303–355
Cerutti A (2008) The regulation of IgA class switching. Nat Rev Immunol 8:421–434
Fagarasan S, Honjo T (2003) Intestinal IgA synthesis: regulation of front-line body defences. Nat Rev Immunol 3:63–72
Fagarasan S, Kawamoto S, Kanagawa O, Suzuki K (2010) Adaptive immune regulation in the gut: T cell-dependent and T cell-independent IgA synthesis. Annu Rev Immunol 28:243–273
Puga I, Cols M, Cerutti A (2010) Innate signals in mucosal immunoglobulin class switching. J Allergy Clin Immunol 126:889–895
McCarthy DD, Chiu S, Gao Y, Summers-deLuca LE, Gommerman JL (2006) BAFF induces a hyper-IgA syndrome in the intestinal lamina propria concomitant with IgA deposition in the kidney independent of LIGHT. Cell Immunol 241:85–94
Tezuka H, Abe Y, Iwata M et al (2007) Regulation of IgA production by naturally occurring TNF/iNOS-producing dendritic cells. Nature 448:929–933
He B, Santamaria R, Xu W et al (2010) The transmembrane activator TACI triggers immunoglobulin class switching by activating B cells through the adaptor MyD88. Nat Immunol 11:836–845
Macpherson AJ, McCoy KD, Johansen FE, Brandtzaeg P (2008) The immune geography of IgA induction and function. Mucosal Immunol 1:11–22
Uren TK, Johansen FE, Wijburg OL, Koentgen F, Brandtzaeg P, Strugnell RA (2003) Role of the polymeric Ig receptor in mucosal B cell homeostasis. J Immunol 170:2531–2539
Coppo R (1988) The pathogenetic potential of environmental antigens in IgA nephropathy. Am J Kidney Dis 12:420–424
Russell MW, Mestecky J, Julian BA, Galla JH (1986) IgA-associated renal diseases: antibodies to environmental antigens in sera and deposition of immunoglobulins and antigens in glomeruli. J Clin Immunol 6:74–86
Smerud HK, Fellstrom B, Hallgren R, Osagie S, Venge P, Kristjansson G (2009) Gluten sensitivity in patients with IgA nephropathy. Nephrol Dial Transplant 24:2476–2481
Sharmin S, Shimizu Y, Hagiwara M, Hirayama K, Koyama A (2004) Staphylococcus aureus antigens induce IgA-type glomerulonephritis in Balb/c mice. J Nephrol 17:504–511
Yamamoto C, Suzuki S, Kimura H, Yoshida H, Gejyo F (2002) Experimental nephropathy induced by Haemophilus parainfluenzae antigens. Nephron 90:320–327
Amore A, Coppo R, Nedrud JG, Sigmund N, Lamm ME, Emancipator SN (2004) The role of nasal tolerance in a model of IgA nephropathy induced in mice by Sendai virus. Clin Immunol 113:101–108
Jessen RH, Emancipator SN, Jacobs GH, Nedrud JG (1992) Experimental IgA-IgG nephropathy induced by a viral respiratory pathogen. Dependence on antigen form and immune status. Lab Invest 67:379–386
Emancipator SN, Gallo GR, Lamm ME (1983) Experimental IgA nephropathy induced by oral immunization. J Exp Med 157:572–582
Coppo R, Mazzucco G, Martina G et al (1989) Gluten-induced experimental IgA glomerulopathy. Lab Invest 60:499–506
Kusano K, Inokuchi A, Fujimoto K et al (2010) Coccoid Helicobacter pylori exists in the palatine tonsils of patients with IgA nephropathy. J Gastroenterol 45:406–412
Coppo R, Camilla R, Amore A et al (2010) Toll-like receptor 4 expression is increased in circulating mononuclear cells of patients with immunoglobulin A nephropathy. Clin Exp Immunol 159:73–81
Duan B, Morel L (2006) Role of B-1a cells in autoimmunity. Autoimmun Rev 5:403–408
Magyarlaki T, Davin JC, Szabados E, Kocsis B, Nagy J (1990) Peripheral B-lymphocyte markers and function in IgA nephropathy. Clin Nephrol 33:123–129
Kodama S, Suzuki M, Arita M, Mogi G (2001) Increase in tonsillar germinal centre B-1 cell numbers in IgA nephropathy (IgAN) patients and reduced susceptibility to Fas-mediated apoptosis. Clin Exp Immunol 123:301–308
Yuling H, Ruijing X, Xiang J et al (2008) CD19 + CD5+ B cells in primary IgA nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol 19:2130–2139
Buck KS, Foster EM, Watson D et al (2002) Expression of T cell receptor variable region families by bone marrow gammadelta T cells in patients with IgA nephropathy. Clin Exp Immunol 127:527–532
Olive C, Allen AC, Harper SJ, Wicks AC, Feehally J, Falk MC (1997) Expression of the mucosal gamma delta T cell receptor V region repertoire in patients with IgA nephropathy. Kidney Int 52:1047–1053
Toyabe S, Harada W, Uchiyama M (2001) Oligoclonally expanding gammadelta T lymphocytes induce IgA switching in IgA nephropathy. Clin Exp Immunol 124:110–117
Horie A, Hiki Y, Odani H et al (2003) IgA1 molecules produced by tonsillar lymphocytes are under-O-glycosylated in IgA nephropathy. Am J Kidney Dis 42:486–496
Inoue T, Sugiyama H, Hiki Y et al (2010) Differential expression of glycogenes in tonsillar B lymphocytes in association with proteinuria and renal dysfunction in IgA nephropathy. Clin Immunol 136:447–455
Huang H, Peng Y, Liu H, Yang X, Liu F (2010) Decreased CD4+CD25+ cells and increased dimeric IgA-producing cells in tonsils in IgA nephropathy. J Nephrol 23:202–209
Harper SJ, Allen AC, Bene MC et al (1995) Increased dimeric IgA-producing B cells in tonsils in IgA nephropathy determined by in situ hybridization for J chain mRNA. Clin Exp Immunol 101:442–448
Coppo R (2010) Can a dysregulated mucosal immune system in IgA nephropathy be controlled by tonsillectomy? Nephrol Dial Transplant 25:2395–2397
Oortwijn BD, Rastaldi MP, Roos A, Mattinzoli D, Daha MR, van Kooten C (2007) Demonstration of secretory IgA in kidneys of patients with IgA nephropathy. Nephrol Dial Transplant 22:3191–3195
van den Wall Bake AW, Daha MR, Evers-Schouten J, van Es LA (1988) Serum IgA and the production of IgA by peripheral blood and bone marrow lymphocytes in patients with primary IgA nephropathy: evidence for the bone marrow as the source of mesangial IgA. Am J Kidney Dis 12:410–414
Harper SJ, Pringle JH, Wicks AC et al (1994) Expression of J chain mRNA in duodenal IgA plasma cells in IgA nephropathy. Kidney Int 45:836–844
Westberg NG, Baklien K, Schmekel B, Gillberg R, Brandtzaeg P (1983) Quantitation of immunoglobulin-producing cells in small intestinal mucosa of patients with IgA nephropathy. Clin Immunol Immunopathol 26:442–445
Roodnat JI, de Fijter JW, van Kooten C, Daha MR, van Es LA (1999) Decreased IgA1 response after primary oral immunization with live typhoid vaccine in primary IgA nephropathy. Nephrol Dial Transplant 14:353–359
de Fijter JW, Eijgenraam JW, Braam CA et al (1996) Deficient IgA1 immune response to nasal cholera toxin subunit B in primary IgA nephropathy. Kidney Int 50:952–961
Layward L, Finnemore AM, Allen AC, Harper SJ, Feehally J (1993) Systemic and mucosal IgA responses to systemic antigen challenge in IgA nephropathy. Clin Immunol Immunopathol 69:306–313
van den Wall Bake AW, Beyer WE, Evers-Schouten JH et al (1989) Humoral immune response to influenza vaccination in patients with primary immunoglobulin A nephropathy. An analysis of isotype distribution and size of the influenza-specific antibodies. J Clin Invest 84:1070–1075
Smith AC, Molyneux K, Feehally J, Barratt J (2006) O-Glycosylation of Serum IgA1 Antibodies against Mucosal and Systemic Antigens in IgA Nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol 17:3520–3528
Barratt J, Eitner F, Feehally J, Floege J (2009) Immune complex formation in IgA nephropathy: a case of the ‘right’ antibodies in the ‘wrong’ place at the ‘wrong’ time? Nephrol Dial Transplant 24:3620–3623
Kunkel EJ, Butcher EC (2003) Plasma-cell homing. Nat Rev Immunol 3:822–829
Batra A, Smith AC, Feehally J, Barratt J (2007) T-cell homing receptor expression in IgA nephropathy. Nephrol Dial Transplant 22:2540–2548
Schena FP, Pastore A, Ludovico N, Sinico RA, Benuzzi S, Montinaro V (1989) Increased serum levels of IgA1-IgG immune complexes and anti-F(ab’)2 antibodies in patients with primary IgA nephropathy. Clin Exp Immunol 77:15–20
Novak J, Julian BA, Tomana M, Mestecky J (2008) IgA glycosylation and IgA immune complexes in the pathogenesis of IgA nephropathy. Semin Nephrol 28:78–87
van der Boog PJ, van Kooten C, de Fijter JW, Daha MR (2005) Role of macromolecular IgA in IgA nephropathy. Kidney Int 67:813–821
Baldree LA, Wyatt RJ, Julian BA, Falk RJ, Jennette JC (1993) Immunoglobulin A-fibronectin aggregate levels in children and adults with immunoglobulin A nephropathy. Am J Kidney Dis 22:1–4
Chowdhury B, Zhang Z, Mukherjee AB (2008) Uteroglobin interacts with the heparin-binding site of fibronectin and prevents fibronectin-IgA complex formation found in IgA-nephropathy. FEBS Lett 582:611–615
Grossetete B, Launay P, Lehuen A, Jungers P, Bach JF, Monteiro RC (1998) Down-regulation of Fc alpha receptors on blood cells of IgA nephropathy patients: evidence for a negative regulatory role of serum IgA. Kidney Int 53:1321–1335
van der Boog PJ, De Fijter JW, Van Kooten C et al (2003) Complexes of IgA with FcalphaRI/CD89 are not specific for primary IgA nephropathy. Kidney Int 63:514–521
Launay P, Grossetete B, Arcos-Fajardo M et al (2000) Fcalpha receptor (CD89) mediates the development of immunoglobulin A (IgA) nephropathy (Berger’s disease). Evidence for pathogenic soluble receptor-Iga complexes in patients and CD89 transgenic mice. J Exp Med 191:1999–2009
Nieuwhof C, Kruytzer M, Frederiks P, van Breda Vriesman PJ (1998) Chronicity index and mesangial IgG deposition are risk factors for hypertension and renal failure in early IgA nephropathy. Am J Kidney Dis 31:962–970
Glassock RJ (2009) Analyzing antibody activity in IgA nephropathy. J Clin Invest 119:1450–1452
Leung JC, Tsang AW, Chan DT, Lai KN (2000) Absence of CD89, polymeric immunoglobulin receptor, and asialoglycoprotein receptor on human mesangial cells. J Am Soc Nephrol 11:241–249
McDonald KJ, Cameron AJ, Allen JM, Jardine AG (2002) Expression of Fc alpha/mu receptor by human mesangial cells: a candidate receptor for immune complex deposition in IgA nephropathy. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 290:438–442
Lai KN (2009) Recent advances in IgA nephropathy. World Scientific, Hackensack
Hiemstra PS, Biewenga J, Gorter A et al (1988) Activation of complement by human serum IgA, secretory IgA and IgA1 fragments. Mol Immunol 25:527–533
Roos A, Bouwman LH, van Gijlswijk-Janssen DJ, Faber-Krol MC, Stahl GL, Daha MR (2001) Human IgA activates the complement system via the mannan-binding lectin pathway. J Immunol 167:2861–2868
Hisano S, Matsushita M, Fujita T, Endo Y, Takebayashi S (2001) Mesangial IgA2 deposits and lectin pathway-mediated complement activation in IgA glomerulonephritis. Am J Kidney Dis 38:1082–1088
Roos A (2006) Glomerular activation of the lectin pathway of complement in IgA nephropathy is associated with more severe renal disease. J Am Soc Nephrol 17:1724–1734
Espinosa M, Ortega R, Gomez-Carrasco JM et al (2009) Mesangial C4d deposition: a new prognostic factor in IgA nephropathy. Nephrol Dial Transplant 24:886–891
Allen AC, Willis FR, Beattie TJ, Feehally J (1998) Abnormal IgA glycosylation in Henoch-Schonlein purpura restricted to patients with clinical nephritis. Nephrol Dial Transplant 13:930–934
Levinsky RJ, Barratt TM (1979) IgA immune complexes in Henoch-Schonlein purpura. Lancet 2:1100–1103
Haddad E, Moura IC, Arcos-Fajardo M et al (2003) Enhanced expression of the CD71 mesangial IgA1 receptor in Berger disease and Henoch-Schonlein nephritis: association between CD71 expression and IgA deposits. J Am Soc Nephrol 14:327–337
Meadow SR, Scott DG (1985) Berger disease: Henoch-Schonlein syndrome without the rash. J Pediatr 106:27–32
Akiyama F, Tanaka T, Yamada R et al (2002) Single-nucleotide polymorphisms in the class II region of the major histocompatibility complex in Japanese patients with immunoglobulin A nephropathy. J Hum Genet 47:532–538
Cao HX, Li M, Nie J, Wang W, Zhou SF, Yu XQ (2008) Human leukocyte antigen DRB1 alleles predict risk and disease progression of immunoglobulin A nephropathy in Han Chinese. Am J Nephrol 28:684–691
Brabcova I, Tesar V, Honsova E et al (2010) Association of advanced vasculopathy and transforming growth factor-beta1 gene expression with immunoglobulin A nephropathy progression. Nephrol Dial Transplant (in press)
Vuong MT, Lundberg S, Gunnarsson I et al (2009) Genetic variation in the transforming growth factor-beta1 gene is associated with susceptibility to IgA nephropathy. Nephrol Dial Transplant 24:3061–3067
Masutani K, Miyake K, Nakashima H et al (2003) Impact of interferon-gamma and interleukin-4 gene polymorphisms on development and progression of IgA nephropathy in Japanese patients. Am J Kidney Dis 41:371–379
Narita I, Kondo D, Goto S et al (2001) Association of gene polymorphism of polymeric immunoglobulin receptor and IgA nephropathy. Intern Med 40:867–872
Shu KH, Lee SH, Cheng CH, Wu MJ, Lian JD (2000) Impact of interleukin-1 receptor antagonist and tumor necrosis factor-alpha gene polymorphism on IgA nephropathy. Kidney Int 58:783–789
Tuglular S, Berthoux P, Berthoux F (2003) Polymorphisms of the tumour necrosis factor alpha gene at position −308 and TNFd microsatellite in primary IgA nephropathy. Nephrol Dial Transplant 18:724–731
Hahn WH, Cho BS, Kim SD, Kim SK, Kang S (2009) Interleukin-1 cluster gene polymorphisms in childhood IgA nephropathy. Pediatr Nephrol 24:1329–1336
Watanabe M, Iwano M, Akai Y et al (2002) Association of interleukin-1 receptor antagonist gene polymorphism with IgA nephropathy. Nephron 91:744–746
Malycha F, Eggermann T, Hristov M et al (2009) No evidence for a role of cosmc-chaperone mutations in European IgA nephropathy patients. Nephrol Dial Transplant 24:321–324
Lau YK, Woo KT, Choong HL et al (2004) Renin-angiotensin system gene polymorphisms: its impact on IgAN and its progression to end-stage renal failure among Chinese in Singapore. Nephron Physiol 97:1–8
Maruyama K, Yoshida M, Nishio H et al (2001) Polymorphisms of renin-angiotensin system genes in childhood IgA nephropathy. Pediatr Nephrol 16:350–355
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, HH., Chu, KH., Yang, YH. et al. Genetics and Immunopathogenesis of IgA Nephropathy. Clinic Rev Allerg Immunol 41, 198–213 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12016-010-8232-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12016-010-8232-0