Abstract
Introduction
Many risk prediction models of diabetes remission after bariatric and metabolic surgery have been proposed. Most models have been created using Roux-en-Y gastric bypass cohorts. However, validation of these models in sleeve gastrectomy (SG) is limited. The objective of our study is to validate the performance of risk prediction models of diabetes remission in obese patients with diabetes who underwent SG.
Method
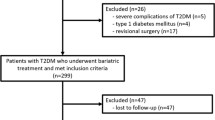
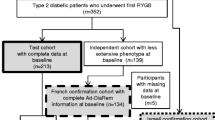
This retrospective cohort study included 128 patients who underwent SG with at least 1 year follow-up from Dec 2011 to Sep 2016 as the validation cohort. A literature review revealed total 11 models with 2 categories (scoring system and logistic regression), which were validated by our study dataset. Discrimination was evaluated by area under the receiver operating characteristic (AUC) while calibration by Hosmer–Lemeshow test and predicted versus observed remission ratio.
Results
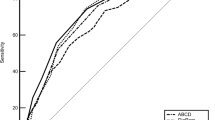
At 1 year after surgery, 71.9% diabetes remission (HbA1c < 6.0 off medication) and 61.4% excess weight loss were observed. Individual metabolic surgery, ABCD, DiaRem, Advanced-DiaRem, DiaBetter, Ana et al., and Dixon et al. models showed excellent discrimination power (AUC > 0.8). In calibration, all models overestimated diabetes remission from 5 to 30% but did not lose their goodness of fit.
Conclusion
This is the first comprehensive external validation of current risk prediction models of diabetes remission at 1 year after SG. Seven models showed excellent predicting power, and scoring models were recommended more because of their easy utility.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mingrone G, Panunzi S, De Gaetano A, et al. Bariatric–metabolic surgery versus conventional medical treatment in obese patients with type 2 diabetes: 5 year follow-up of an open-label, single-centre, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2015;386(9997):964–73.
Cummings DE, Arterburn DE, Westbrook EO, et al. Gastric bypass surgery vs intensive lifestyle and medical intervention for type 2 diabetes: the CROSSROADS randomised controlled trial. Diabetologia. 2016;59(5):945–53.
Schauer PR, Bhatt DL, Kirwan JP, et al. Bariatric surgery versus intensive medical therapy for diabetes—5-year outcomes. N Engl J Med. 2017;376(7):641–51.
Ikramuddin S, Korner J, Lee W, et al. Lifestyle intervention and medical management with vs without Roux-en-Y gastric bypass and control of hemoglobin a1c, ldl cholesterol, and systolic blood pressure at 5 years in the diabetes surgery study. JAMA. 2018;319(3):266–78.
Vidal P, Ramón JM, Goday A, et al. Laparoscopic gastric bypass versus laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy as a definitive surgical procedure for morbid obesity. Mid-term results. Obes Surg. 2013;23(3):292–9.
Schauer PR, Bhatt DL, Kirwan JP, et al. Bariatric surgery versus intensive medical therapy for diabetes — 3-year outcomes. N Engl J Med. 2014;370(21):2002–13.
Peterli R, Wölnerhanssen BK, Vetter D, et al. Laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy versus Roux-Y-gastric bypass for morbid obesity—3-year outcomes of the prospective randomized Swiss Multicenter Bypass or Sleeve Study (SM-BOSS). Ann Surg. 2017;265(3):466–73.
Weinstein AL, Marascalchi BJ, Spiegel MA, et al. Patient preferences and bariatric surgery procedure selection; the need for shared decision-making. Obes Surg. 2014;24(11):1933–9.
Aminian A, Brethauer SA, Andalib A, et al. Can sleeve gastrectomy “cure” diabetes? Long-term metabolic effects of sleeve gastrectomy in patients with type 2 diabetes. Ann Surg. 2016;264(4):674–81.
Coleman KJ, Haneuse S, Johnson E, et al. Long-term microvascular disease outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes after bariatric surgery: evidence for the legacy effect of surgery. Diabetes Care. 2016;39(8):1400–7.
Rubino F, Nathan DM, Eckel RH, et al. Metabolic surgery in the treatment algorithm for type 2 diabetes: a joint statement by international diabetes organizations. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2016;12(6):1144–62.
Wang G-F, Yan Y-X, Xu N, et al. Predictive factors of type 2 diabetes mellitus remission following bariatric surgery: a meta-analysis. Obes Surg. 2015;25(2):199–208.
Fang Y-L, Lee W-J. Predictors for type 2 diabetes mellitus remission after metabolic/bariatric surgery. Ann Laparosc Endosc Surg 2017; 2(1).
Adams S, Salhab M, Hussain Z, et al. Preoperatively determinable factors predictive of diabetes mellitus remission following Roux-en-Y gastric bypass: a review of the literature. Acta Diabetol. 2013;50(4):475–8.
Zhang R, Borisenko O, Telegina I, et al. Systematic review of risk prediction models for diabetes after bariatric surgery. BJS. 2016;103(11):1420–7.
Lee W-J, Hur KY, Lakadawala M, et al. Predicting success of metabolic surgery: age, body mass index, C-peptide, and duration score. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2013;9(3):379–84.
Panunzi S, Carlsson L, De Gaetano A, et al. Determinants of diabetes remission and glycemic control after bariatric surgery. Diabetes Care 2015:dc150575.
Khorgami Z, Shoar S, Andalib A, et al. Trends in utilization of bariatric surgery, 2010-2014: sleeve gastrectomy dominates. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2017;13(5):774–8.
Angrisani L, Santonicola A, Iovino P, et al. Bariatric surgery and endoluminal procedures: IFSO Worldwide Survey 2014. Obes Surg. 2017;27(9):2279–89.
Batterham RL, Cummings DE. Mechanisms of diabetes improvement following bariatric/metabolic surgery. Diabetes Care. 2016;39(6):893–901.
Cho YM. A gut feeling to cure diabetes: potential mechanisms of diabetes remission after bariatric surgery. Diabetes Metab J. 2014;38(6):406–15.
Buse JB, Caprio S, Cefalu WT, et al. How do we define cure of diabetes? Diabetes Care. 2009;32(11):2133–5.
Ugale S, Gupta N, Modi KD, et al. Prediction of remission after metabolic surgery using a novel scoring system in type 2 diabetes–a retrospective cohort study. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2014;13(1):89.
Alba AC, Agoritsas T, Walsh M, et al. Discrimination and calibration of clinical prediction models: users’ guides to the medical literature. Jama. 2017;318(14):1377–84.
Moons KG, Kengne AP, Woodward M, et al. Risk prediction models: I. development, internal validation, and assessing the incremental value of a new (bio) marker. Heart. 2012;98(9):683–90.
Hosmer Jr DW, Lemeshow S, Sturdivant RX. Applied logistic regression. Vol. 398: John Wiley & Sons, 2013.
Youden WJ. Index for rating diagnostic tests. Cancer. 1950;3(1):32–5.
Aminian A, Brethauer SA, Andalib A, et al. Individualized metabolic surgery score: procedure selection based on diabetes severity. Ann Surg. 2017;266(4):650–7.
Still CD, Wood GC, Benotti P, et al. Preoperative prediction of type 2 diabetes remission after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery: a retrospective cohort study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2014;2(1):38–45.
Aron-Wisnewsky J, Sokolovska N, Liu Y, et al. The advanced-DiaRem score improves prediction of diabetes remission 1 year post-Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. Diabetologia. 2017;60(10):1892–902.
Pucci A, Tymoszuk U, Cheung W, et al. Type 2 diabetes remission 2 years post Roux-en-Y gastric bypass and sleeve gastrectomy: the role of the weight loss and comparison of DiaRem and DiaBetter scores. Diabet Med 2017.
Robert M, Ferrand-Gaillard C, Disse E, et al. Predictive factors of type 2 diabetes remission 1 year after bariatric surgery: impact of surgical techniques. Obes Surg. 2013;23(6):770–5.
Dixon J, Hur KY, Lee WJ, et al. Gastric bypass in type 2 diabetes with BMI < 30: weight and weight loss have a major influence on outcomes. Diabet Med 2013; 30(4).
Hayes MT, Hunt LA, Foo J, et al. A model for predicting the resolution of type 2 diabetes in severely obese subjects following Roux-en Y gastric bypass surgery. Obes Surg. 2011;21(7):910–6.
Park JY, Kim YJ. Prediction of diabetes remission in morbidly obese patients after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. Obes Surg. 2016;26(4):749–56.
Ramos-Levi AM, Matia P, Cabrerizo L, et al. Statistical models to predict type 2 diabetes remission after bariatric surgery 预测 2 型糖尿病患者减肥手术后缓解情况的统计学模型. J diabetes. 2014;6(5):472–7.
Lee W-J, Almulaifi A, Tsou JJ, et al. Laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy for type 2 diabetes mellitus: predicting the success by ABCD score. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2015;11(5):991–6.
Lee W-J, Chong K, Chen S-C, et al. Preoperative prediction of type 2 diabetes remission after gastric bypass surgery: a comparison of DiaRem scores and ABCD scores. Obes Surg. 2016;26(10):2418–24.
Cotillard A, Poitou C, Duchâteau-Nguyen G, et al. Type 2 diabetes remission after gastric bypass: what is the best prediction tool for clinicians? Obes Surg. 2015;25(7):1128–32.
Lee W-J, Chong K, Aung L, et al. Metabolic surgery for diabetes treatment: sleeve gastrectomy or gastric bypass? World J Surg. 2017;41(1):216–23.
Chen J-C, Hsu N-Y, Lee W-J, et al. Prediction of type 2 diabetes remission after metabolic surgery: a comparison of the individualized metabolic surgery score and the ABCD score. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2018;14:640–5.
Craig Wood G, Horwitz D, Still CD, et al. Performance of the DiaRem score for predicting diabetes remission in two health systems following bariatric surgery procedures in Hispanic and non-Hispanic white patients. Obes Surg. 2018;28(1):61–8.
Ahuja A, Tantia O, Chaudhuri T, et al. Predicting remission of diabetes post metabolic surgery: a comparison of ABCD, diarem, and DRS scores. Obes Surg. 2018:1–7.
Cho J-M, Kim HJ, Menzo EL, et al. Effect of sleeve gastrectomy on type 2 diabetes as an alternative treatment modality to Roux-en-Y gastric bypass: systemic review and meta-analysis. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2015;11(6):1273–80.
Arterburn D, Gupta A. Comparing the outcomes of sleeve gastrectomy and Roux-en-Y gastric bypass for severe obesity. Jama. 2018;319(3):235–7.
Acknowledgements
This manuscript was edited by Wallace Academic Editing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 139 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shen, SC., Wang, W., Tam, KW. et al. Validating Risk Prediction Models of Diabetes Remission After Sleeve Gastrectomy. OBES SURG 29, 221–229 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11695-018-3510-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11695-018-3510-7