Abstract
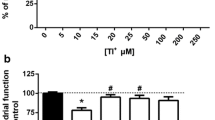
S-sulfo-cysteine (SSC) is an agonist of glutamate receptors which could be involved in cysteine-induced neurotoxicity. Here we analyzed SSC by HPLC and demonstrated that the concentration of SSC in cortex of cysteine-injected rats increased to 1.4 μM, about four times the value of control rats. The neurotoxic effect of SSC was evaluated in slice cultures of rat hippocampus and compared to NMDA and cysteine. The neurotoxicity threshold of SSC was well above the tissue concentration. Our results show that SSC increases in neonatal rat brain after cysteine injection but reaches a tissue concentration far below concentrations that induce neurotoxicity in vitro. Thus, even if all the tissue SSC after cysteine injection was extracellular it would be below the threshold for toxicity, indicating that SSC is not a main excitotoxin involved in cysteine toxicity.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Olney JW, Ho OL (1970) Brain damage in infant mice following oral intake of glutamate, aspartate or cysteine. Nature 227:609–611
Olney JW, Ho OL, Rhee V (1971) Cytotoxic effects of acidic and sulfur containing amino acids on the infant mouse central nervous system. Exp Brain Res 14:61–76
Olney JW, Ho OL, Rhee V, Schainker B (1972) Cysteine-induced brain damage in infant and fetal rodents. Brain Res 45:309–313
Olney JW, Zorumski C, Price MT, Labruyere J (1990) L-Cysteine, a bicarbonate-sensitive endogenous excitotoxin. Science 248:596–599
Sharpe LG, Onley JW, Ohlendorf C, Lyss A, Zimmerman M, Gale B (1975) Brain damage and associated behavioral deficit following the administration of L-cysteine to infant rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 3:291–298
Misra CH (1989) Is a certain amount of cysteine prerequiste to produce brain damage in neonatal rats. Neurochem Res 14:253–257
Fonnum F, Malthe-Sorenssen D, Lund-Karlsen R, Oddan E (1992) Changes in neurotransmitter parameters in the brain induced by L-cysteine injections in the young rat. Brain Res 579:74–78
Perry TL, Norman MG, Young VW, Whiting S, Crichton JU, Hansen S, Kish SJ (1985) Hallervordon-Spatz disease: cysteine accumulation and cysteine dioxygenase deficiency in the globus pallidus. Ann Neurol 18:482–489
Heafield MT, Fearn S, Steventon GB, Waring RH, Williams AC, Sturman SG (1990) Plasma cysteine and sulphate levels in patients with Motor neuron, Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci Lett 110:216–220
Steventon GB, Waring RH, Heafield MT, Sturman SG, Williams AC (1991) Cystine, sulfate, and ALS. Neurological 41:1851–1852
Landolt H, Lutz TW, Langemann H, Stäuble D, Mendelowitsch A, Gratzl O, Honegger CG (1992) Extracellular antioxidants and amino acids in the cortex of the rat: monitoring by microdialysis of early ischemic changes. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 12:96–102
Slivka A, Cohen G (1993) Brain ischemia markedly elevates levels of the neuroactive amino acid, cysteine. Brain Res 608:33–37
Lipton SA (1996) Similarity of neuronal cell injury and death in AIDS dementia and focal cerebral ischemia: potential treatment with NMDA open-channel blockers and nitric oxide-related species. Brain Pathol 6:507–517
Montine TJ, Amarnath V, Picklo MJ, Sidell KR, Zhang J, Graham DG (2000) Dopamine mercapturate can augment dopaminergic neurodegeneration. Drug Metab Rev 32:363–376
Pace JR, Martin BM, Paul SM, Rogawski MA (1992) High concentrations of neutral amino acids activate NMDA receptor currents in rat hippocampal neurons. Neurosci Lett 141:97–100
Mudd SH, Irreverre F, Laster L (1967) Sulfite oxidase deficiency in man: demonstration of the enzymatic defect. Science 156:1599–1602
Irreverre F, Mudd SH, Heizer WD, Laster L (1967) Sulfite oxidase deficiency: studies of a patient with mental retardation, dislocated ocular lenses, and abnormal urinary excretion of S-sulfo-L-cysteine, sulfite, and thiosulfate. Biochem Med 1:187–217
Shih VE, Abroms IF, Johnson JL, Carney M, Mandell R, Robb RM, Cloherty JP, Rajagopalan KV (1977) Sulfite oxidase deficiency: biochemical and clinical investigations of a hereditary metabolic disorder in sulfur metabolism. N Engl J Med 279:1022–1028
Eyaid WM, Al-Nouri DM, Rashed MS, Al-Rifai MT, Wakeel AS (2005) An inborn error of metabolism presenting as hypoxic-ischemic insult. Pediatr Neurol 32:134–136
Seidahmed MZ, Alyamani EA, Rashed MS, Saadallah AA, Abdelbasit OB, Shaheed MM, Rasheed A, Hamid FA, Sabry MA (2005) Total truncation of the molybdopterin/dimerization domains of SUOX protein in an Arab family with isolated sulfite oxidase deficiency. Am J Med Genet A 136:205–209
Pullan LM, Olney JW, Price MT, Compton RP, Hood WF, Michel J, Monahan JB (1987) Excitatory amino acid receptor potency and subclass specificity of sulfur-containing amino acids. J Neurochem 49:1301–1307
Curtis DR, Watkins JC (1960) The excitation and depression of spinal neurons by structurally related amino acids. J Neurochem 6:117–141
Curtis DR, Watkins JC (1963) Acidic amino acids with strong excitatory actions on mammalian neurons. J Physiol 66:1–14
Mewett KN, Oakes DJ, Olverman HJ, Smith DAS, Watkins JC (1983) Pharmacology of the excitatory actions of sulphonic and sulphinic amino acids. In: Mandel P, De Feudis FV (eds) CNS receptors-from molecular pharmacology to behaviour, Raven Press, New York, pp 163–174
Olney JW, Misra CH, Gubareff T (1975) Cysteine-S-Sulfate: Brain damaging metabolite in sulfite oxidase deficiency. J Neuropath Exp Neurol 34:167–177
Moore W, Wiener HL, Meister A (1987) Inactivation of Gamma-glutamylcysteine synthetase, but not of glutamine synthetase, by S-sulfocysteine and S-sulfohomocysteine. J Biol Chem 262:16771–16777
Xia W, Sandberg M, Weber SG (1998) Comparision of anion-exchange and ion-modified reversed-phase liquid chromatography for the determination of S-sulfocysteine. J Chromatogr B 705:251–259
Lehmann A, Hagberg H, Orwar O, Sandberg M (1993) Cysteine sulphinate and cysteate: mediators of cysteine toxicity in the neonatal rat brain? Eur J Neurosci 5:1398–1412
Stoppini L, Buchs PA, Muller D (1991) A simple method for organotypic cultures of nervous tissue. J Neurosci Methods 37:173–182
Tranberg M, Stridh MH, Guy Y, Jilderos B, Wigström H, Weber SW, Sandberg M (2004) NMDA-receptor mediated efflux of N-acetylaspartate: physiological and/or pathological importance? Neurochem Int 45:1195–1204
Lindroth P, Mopper K (1979) High performance liquid chromatographic determination of subpicomole amounts of amino acids by precolumn fluorescence derivatization with o-phthalaldehyde. Anal Chem 51:1667–1674
Sandberg M, Butcher S, Hagberg H (1986) Extracellular overflow of neuroactive amino acids during severe insulin-induced hypoglycemia-in vivo dialysis of the rat hippocampus. J Neurochem 47:178–184
Xia W, Sandberg M, Weber SG (1999) Development of a liquid chromatographic method for picomole determination of S-sulfocysteine in trifluroacetic acid extract of neonatal rat brain. J Pharmaceut Biomed Anal 19:261–268
Noraberg J, Kristensen BW, Zimmer J (1999) Markers for neuronal degeneration in organotypic slice cultures. Brain Res Brain Res Protoc 3:278–290
Vornov JJ, Park J, Thomas AG (1998) Regional vulnerability to endogenous and exogenous oxidative stress in organotypic hippocampal culture. Exp Neurol 149:109–122
Abbas A-K, Jardemark K, Lehmann A, Weber SG, Sandberg M (1997) Bicarbonate-sensitive cysteine induced elevation of extracellular aspartate and glutamate in rat hippocampus in vitro. Neurochem Int 30:253–259
Patneau DK, Mayer ML (1990) Structure-activity relationships for amino acid transmitter candidates acting at N-methyl-D-aspartate and quisqualate receptors. J Neurosci 10:2385–2399
Olverman HJ, Jones AW, Mewett KN, Watkins JC (1988) Structure/Activity Relations of N -methyl-D-aspartate receptor ligands as studied by their inhibition of [3H]-2-amino-5-phosphonopentanoic acid binding in rat brain membrane. Neuroscience 26:17–31
Rothman SM, Olney JW (1987) Excitotoxicity and the NMDA receptor. Trends Neurosci. 10:299–302
Olney JW, Labruyere J, Price MT (1989) Pathological changes induced in cerebrocortical neurons by phencyclidine and related drugs. Science 244:1360–1362
Auer RN, Coulter KC (1994) The nature and time course of neuronal vacuolation induced by the N-methyl-D-aspartate antagonist MK-801. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 87:1–7
Fix AS, Wozniak DF, Truex LL, McEwen M, Miller JP, Olney JW (1995) Quantitative analysis of factors influencing neuronal necrosis induced by MK-801 in the rat posterior cingulate/retrosplenial cortex. Brain Res 696:194–204
Ishihara K, Alkondon M, Montes JG, Albuquerque EX (1995) Ontogenically related properties of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors in rat hippocampal neurons and the age-specific sensitivity of developing neurons to lead. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 273:1459–1470
Bruce AJ, Sakhi S, Schreiber SS, Baudry M (1995) Development of kainic acid and N-methyl-D-aspartic acid toxicity in organotypic hippocampal cultures. Exp Neurol 132:209–219
Mathisen GA, Fonnum F, Paulsen RE (1996) Contributing mechanisms for cysteine excitotoxicity in cultured cerebellar granule cells. Neurochem Res 21:293–298
Max B (1991) This and that: the neurotoxicity of carbon diaoxide. Trends Pharmacol Sci 12:408–411
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge the financial support of the National Institute of Health (GM 44842), the Swedish Research Council/Medicine, the Swedish Alzheimer Foundation and the foundations of Åhlén, Magn. Bergvall, Sigurd & Elsa Golje, Wilhelm & Martina Lundgren, Märtha & Gustaf Ågren and Herbert & Karin Jacobsson.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Special issue article in honor of Dr. Frode Fonnum.
Part of this work has been submitted as an abstract and presented as a poster to the 7th Biennial Meeting of the Asian Pacific Society for Neurochemistry (APSN) 2–5 July 2006.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abbas, AK., Xia, W., Tranberg, M. et al. S-Sulfo-Cysteine is an Endogenous Amino Acid in Neonatal Rat Brain but an Unlikely Mediator of Cysteine Neurotoxicity. Neurochem Res 33, 301–307 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-007-9441-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-007-9441-7