Abstract
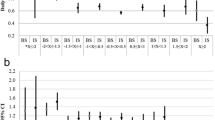
Stroke was demonstrated to correlate with seasonal variation. However, the relevant studies were incongruous. To better understand the rules of seasonal impact on ischemic stroke (IS) patients, we performed this meta-analysis. We systematically searched relevant observational studies in Pubmed, Web of science and Embase from January 1, 1980, to November 1, 2017, in English. Patients included in this study were adults who suffered from IS. Stata version 12.0 software was used to pool useful data and calculate incidence rate ratios (IRRs) and their 95% confidence intervals (CIs). We also performed heterogeneity and sensitivity analyses and evaluated publication bias. Thirty-three observational studies involving 234,196 participants were incorporated into the meta-analysis. Summer and December were regarded as reference, respectively. The IRRs were calculated showing: IRRWinter 1.05 (95% CI 1.04–1.07), IRRAutumn 1.03 (95% CI 1.02–1.04), IRRSpring 1.02 (95% CI 1.01–1.03). No obvious difference existed among 12 months. Stratified analyses on Köppen classification were also conducted. Between-study heterogeneity was discovered; however, predefined stratified analyses and meta-regression could not reduce this heterogeneity. Our meta-analysis has revealed very little seasonal variation in the overall study. Both cold and hot months may be high risky for IS after stratified by Köppen Climate Classification. Thus, a rationale to environmental setting of risky patient management could be provided. More studies with specific assessments are warranted for further comprehensive investigation.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, N., Feigin, V., Bennett, D., Broad, J., Pledger, M., Anderson, C., et al. (2004). Diurnal, weekly, and seasonal variations in stroke occurrence in a population-based study in Auckland, New Zealand. The New Zealand Medical Journal, 117(1202), U1078.
Anlar, O., Tombul, T., Unal, O., & Kayan, M. (2002). Seasonal and environmental temperature variation in the occurrence of ischemic strokes and intracerebral hemorrhages in a Turkish adult population. International Journal of Neuroscience, 112(8), 959–963. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207450290025969.
Ayse, P. T. A., Bilen, S., Arli, B., Oztekin, N., & F., A. (2014). Hospital based epidemiologic analysis of Turkish patients with acute ischemic stroke. GAZZ MED ITAL - ARCH SCI MED, 173(3), 103–107.
Bahonar, A., Khosravi, A., Khorvash, F., Maracy, M., & Saadatnia, M. (2017). Seasonal and monthly variation in stroke and its subtypes-10 year hospital-based study. Mater Sociomed, 29(2), 119–123. https://doi.org/10.5455/msm.2017.29.119-123.
Bhatnagar, A. (2017). Environmental determinants of cardiovascular disease. Circulation Research, 121(2), 162–180. https://doi.org/10.1161/circresaha.117.306458.
Biller, J., Jones, M. P., Bruno, A., Adams, H. P. Jr., & Banwart, K. (1988). Seasonal variation of stroke-does it exist? Neuroepidemiology, 7(2), 89–98.
Cao, Y., Wang, X., Zheng, D., Robinson, T., Hong, D., Richtering, S., et al. (2016). Air pressure, humidity and stroke occurrence: A systematic review and meta-analysis. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 13(7), 675. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph13070675.
Chen, G., Zhang, Y., Song, G., Jiang, L., Zhao, N., Chen, B., et al. (2007). Is diurnal temperature range a risk factor for acute stroke death? International Journal of Cardiology, 116(3), 408–409. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijcard.2006.03.067.
Christensen, A., Rasmussen, L., Baker, M., Lip, G., Dethlefsen, C., & Larsen, T. (2012). Seasonality, incidence and prognosis in atrial fibrillation and stroke in Denmark and New Zealand. BMJ Open. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2012-001210.
Cowperthwaite, M. C., & Burnett, M. G. (2011). An analysis of admissions from 155 United States hospitals to determine the influence of weather on stroke incidence. Journal of Clinical Neuroscience, 18(5), 618–623. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jocn.2010.08.035.
Coxon, T., Goldstein, L., & Odhiambo, B. K. (2018). Analysis of spatial distribution of trace metals, PCB, and PAH and their potential impact on human health in Virginian Counties and independent cities, USA. Environmental Geochemistry and Health. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-018-0172-2.
Crabbe, H. (2012). Risk of respiratory and cardiovascular hospitalisation with exposure to bushfire particulates: New evidence from Darwin, Australia. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 34(6), 697–709.
Davies, B. E. (2015). The UK geochemical environment and cardiovascular diseases: magnesium in food and water. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 37(3), 411–427.
Díaz, A., Gerschcovich, E. R., Díaz, A. A., Antía, F., & Gonorazky, S. (2013). Seasonal variation and trends in stroke hospitalizations and mortality in a south american community hospital. Journal of Stroke and Cerebrovascular Diseases, 22(7), e66–e69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2012.04.007.
Dubey, D., Sawhney, A., Kavishwar, A., Pande, S., & Dubey, D. (2011). A study of anatomical, seasonal and diurnal variation in the occurrence of ischemic stroke. International Journal of Collaborative Research on Internal Medicine & Public Health, 3(10), 781–788.
Feigin, V. L., & Nikitin, Y. P. (1998). Seasonal variation in the occurrence of ischemic stroke and subarachnoid hemorrhage in Siberia, Russia. A population-based study. European Journal of Neurology, 5, 23–27.
Field, T. S., & Hill, M. D. (2002). Weather, chinook, and stroke occurrence. Stroke, 33(7), 1751–1757. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.STR.0000020384.92499.59.
Frost, L., Vukelic Andersen, L., Mortensen, L. S., & Dethlefsen, C. (2006). Seasonal variation in stroke and stroke-associated mortality in patients with a hospital diagnosis of nonvalvular atrial fibrillation or flutter. A population-based study in Denmark. Neuroepidemiology, 26(4), 220–225. https://doi.org/10.1159/000092796.
Fustinoni, O., Saposnik, G., Esnaola y Rojas, M. M., Lakkis, S. G., Sposato, L. A., & ReNACer Investigators. (2013). Higher frequency of atrial fibrillation linked to colder seasons and air temperature on the day of ischemic stroke onset. Journal of Stroke and Cerebrovascular Diseases, 22(4), 476–481. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2013.03.009.
Gill, J. S., Davies, P., Gill, S. K., & Beevers, D. G. (1988). Wind-chill and the seasonal variation of cerebrovascular disease. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology, 41(3), 225–230.
Goggins, W. B., Woo, J., Ho, S., Chan, E. Y., & Chau, P. H. (2012). Weather, season, and daily stroke admissions in Hong Kong. International Journal of Biometeorology, 56(5), 865–872. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00484-011-0491-9.
Gomes, J., Damasceno, A., Carrilho, C., Lobo, V., Lopes, H., Madede, T., et al. (2014). The effect of season and temperature variation on hospital admissions for incident stroke events in Maputo, Mozambique. Journal of Stroke and Cerebrovascular Diseases, 23(2), 271–277.
Han, M. H., Yi, H. J., Kim, Y. S., & Kim, Y. S. (2015). Effect of seasonal and monthly variation in weather and air pollution factors on stroke incidence in Seoul, Korea. Stroke, 46(4), 927–935. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.114.007950.
Hopstock, L. A., Barnett, A. G., Bonaa, K. H., Mannsverk, J., Njolstad, I., & Wilsgaard, T. (2013). Seasonal variation in cardiovascular disease risk factors in a subarctic population: The Tromso Study 1979–2008. Journal of Epidemiology and Community Health, 67(2), 113–118. https://doi.org/10.1136/jech-2012-201547.
Hori, A., Hashizume, M., Tsuda, Y., Tsukahara, T., & Nomiyama, T. (2012). Effects of weather variability and air pollutants on emergency admissions for cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases. International Journal of Environmental Health Research, 22(5), 416–430. https://doi.org/10.1080/09603123.2011.650155.
Iwamoto, J., Takeda, T., & Matsumoto, H. (2012). Sunlight exposure is important for preventing hip fractures in patients with Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, or stroke. Acta Neurologica Scandinavica, 125(4), 279–284. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0404.2011.01555.x.
Jakovljević, D., Salomaa, V., Sivenius, J., Tamminen, M., Sarti, C., Salmi, K., et al. (1996). Seasonal variation in the occurrence of stroke in a Finnish adult population. Stroke, 27(10), 1774–1779.
Jauch, E. C., Saver, J. L., Adams, H. P., Jr., Bruno, A., Connors, J. J., Demaerschalk, B. M., et al. (2013). Guidelines for the early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke: A guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke, 44(3), 870–947. https://doi.org/10.1161/STR.0b013e318284056a.
Johnson, W., Onuma, O., Owolabi, M., & Sachdev, S. (2016). Stroke: A global response is needed. Bulletin of the World Health Organization, 94(9), 634–634a. https://doi.org/10.2471/blt.16.181636.
Karagiannis, A., Tziomalos, K., Mikhailidis, P. D., Semertzidis, P., Kountana, E., Kakafika, I. A., et al. (2010). Seasonal variation in the occurrence of stroke in Northern Greece: A 10 year study in 8204 patients. Neurological Research, 32(3), 326–331. https://doi.org/10.1179/174313208X331608.
Kawahara, J., Sano, H., Fukuzaki, H., Saito, K., & Hirouchi, H. (1989). Acute effects of exposure to cold on blood pressure, platelet function and sympathetic nervous activity in humans. American Journal of Hypertension, 2(9), 724–726.
Keatinge, W. R., Coleshaw, S. R., Cotter, F., Mattock, M., Murphy, M., & Chelliah, R. (1984). Increases in platelet and red cell counts, blood viscosity, and arterial pressure during mild surface cooling: Factors in mortality from coronary and cerebral thrombosis in winter. British Medical Journal (Clinical Research Ed.), 289(6456), 1405–1408.
Kelly-Hayes, M., Wolf, P. A., Kase, C. S., Brand, F. N., McGuirk, J. M., & D’Agostino, R. B. (1995). Temporal patterns of stroke onset. The Framingham study. Stroke, 26(8), 1343–1347.
Kent, S. T., McClure, L. A., Judd, S. E., Howard, V. J., Crosson, W. L., Al-Hamdan, M. Z., et al. (2013). Short- and long-term sunlight radiation and stroke incidence. Annals of Neurology, 73(1), 32–37. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.23737.
Khan, F. A., Engstrom, G., Jerntorp, I., Pessah-Rasmussen, H., & Janzon, L. (2005). Seasonal patterns of incidence and case fatality of stroke in Malmo, Sweden: The STROMA study. Neuroepidemiology, 24(1–2), 26–31. https://doi.org/10.1159/000081046.
Khan, W. M., Khan, M., & Shah, F. (2017). Seasonal variations in stroke: A study in a teaching hospital of khyber pakhtunkhwa. Journal of Medical Sciences (Peshawar), 25(3), 292–296.
Kyobutungi, C., Grau, A., Stieglbauer, G., & Becher, H. (2005). Absolute temperature, temperature changes and stroke risk: A case-crossover study. European Journal of Epidemiology, 20(8), 693–698. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10654-005-0703-x.
Lai, P. M., Dasenbrock, H., & Du, R. (2014). The association between meteorological parameters and aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: A nationwide analysis. PLoS ONE, 9(11), e112961. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0112961.
Lee, H., Hu, C., Chen, C., & Lin, H. (2008). Seasonal variation in ischemic stroke incidence and association with climate: A six-year population-based study. Chronobiology International, 25(6), 938–949.
Lichtman, J. H., Leifheit-Limson, E. C., Jones, S. B., Wang, Y., & Goldstein, L. B. (2016). Average temperature, diurnal temperature variation, and stroke hospitalizations. Journal of Stroke and Cerebrovascular Diseases, 25(6), 1489–1494. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2016.02.037.
Lim, J. S., Kwon, H. M., Kim, S. E., Lee, J., Lee, Y. S., & Yoon, B. W. (2017). Effects of temperature and pressure on acute stroke incidence assessed using a Korean nationwide insurance database. Journal of Stroke, 19(3), 295–303. https://doi.org/10.5853/jos.2017.00045.
Loughnan, M., Tapper, N., & Loughnan, T. (2014). The impact of “unseasonably” warm spring temperatures on acute myocardial infarction hospital admissions in Melbourne, Australia: A city with a temperate climate. Journal of Environmental and Public Health, 2014, 483785. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/483785.
Magalhães, R., Silva, M. C., Correia, M., & Bailey, T. (2011). Are stroke occurrence and outcome related to weather parameters? Results from a population-based study in Northern Portugal. Cerebrovascular Diseases, 32(6), 542–551.
Mao, Y., Schnytzer, Y., Busija, L., Churilov, L., Davis, S., & Yan, B. (2015). “MOONSTROKE”: Lunar patterns of stroke occurrence combined with circadian and seasonal rhythmicity—a hospital based study. Chronobiology International, 32(7), 881–888. https://doi.org/10.3109/07420528.2015.1049614.
Matsumoto, M., Ishikawa, S., & Kajii, E. (2010). Cumulative effects of weather on stroke incidence: A multi-community cohort study in Japan. Journal of Epidemiology, 20(2), 136–142.
Mostofsky, E., Wilker, E. H., Schwartz, J., Zanobetti, A., Gold, D. R., Wellenius, G. A., et al. (2014). Short-term changes in ambient temperature and risk of ischemic stroke. Cerebrovascular Diseases Extra, 4(1), 9–18. https://doi.org/10.1159/000357352.
Myint, P. K., Vowler, S. L., Woodhouse, P. R., Redmayne, O., & Fulcher, R. A. (2007). Winter excess in hospital admissions, in-patient mortality and length of acute hospital stay in stroke: A hospital database study over six seasonal years in Norfolk, UK. Neuroepidemiology, 28(2), 79–85. https://doi.org/10.1159/000098550.
Neuberger, J. S., Hu, S. C., Drake, K. D., & Jim, R. (2009). Potential health impacts of heavy-metal exposure at the Tar Creek Superfund site, Ottawa County, Oklahoma. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 31(1), 47–59.
Oberg, A., Ferguson, J., McIntyre, L., & Horner, R. (2000). Incidence of stroke and season of the year: Evidence of an association. American Journal of Epidemiology, 152(6), 558–564.
Ogata, T., Kimura, K., Minematsu, K., Kazui, S., & Yamaguchi, T. (2004). Variation in ischemic stroke frequency in Japan by season and by other variables. Journal of the Neurological Sciences, 225(1–2), 85–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jns.2004.07.002.
Palm, F., Dos Santos, M., Urbanek, C., Greulich, M., Zimmer, K., Safer, A., et al. (2013). Stroke seasonality associations with subtype, etiology and laboratory results in the Ludwigshafen Stroke Study (LuSSt). European Journal of Epidemiology, 28(5), 373–381. https://doi.org//10.1007/s10654-013-9772-4 .
Raj, K., Bhatia, R., Prasad, K., Srivastava, M. V., Vishnubhatla, S., & Singh, M. B. (2014). Seasonal differences and circadian variation in stroke occurrence and stroke subtypes. Journal of Stroke and Cerebrovascular Diseases, 24(1), 10–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2014.07.051.
Ricci, S., Celani, M. G., Vitali, R., Rosa, F. L., Righetti, E., & Duca, E. (1992). Diurnal and seasonal variations in the occurrence of stroke: A community-based study. Neuroepidemiology, 11, 59–64.
Rothwell, P. M., Wroe, S. J., Slattery, J., Warlow, C. P. (1996). Is stroke incidence related to season or temperature? The Lancet, 347(9006), 934–936.
Rubel, F., Brugger, K., Haslinger, K., & Auer, I. (2017). The climate of the European Alps: Shift of very high resolution Köppen–Geiger climate zones 1800–2100. Meteorologische Zeitschrift, 26(2), 115–125. https://doi.org/10.1127/metz/2016/0816.
Sharma, N., Lewsey, J., Inglis, S., & Moinuddin, A. (2015). Effect of seasonal variation on the frequency of incident stroke hospitalizations in Scotland. Saudi Journal for Health Sciences, 4(1), 23. https://doi.org/10.4103/2278-0521.151405.
Shinkawa, A., Ueda, K., Hasuo, Y., Kiyohara, Y., & Fujishima, M. (1990). Seasonal variation in stroke incidence in Hisayama, Japan. Stroke, 21, 1262–1267.
Shiue, I., & Matzarakis, A. (2011). When stroke epidemiology meets weather and climate: A heat exposure index from human biometeorology. International Journal of Stroke, 6(2), 176. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1747-4949.2010.00576.x.
Shigematsu, K., Watanabe, Y., Nakano, H., & Kyoto Stroke Registry Committee. (2015). Higher ratio of ischemic stroke to hemorrhagic stroke in summer. Acta Neurologica Scandinavica, 132(6), 423–429. https://doi.org/10.1111/ane.12412.
Sipilä, J. O., Ruuskanen, J. O., Kauko, T., Rautava, P., & Kyto, V. (2016). Seasonality of stroke in Finland. Annals of Medicine, 49(4), 310–318. https://doi.org/10.1080/07853890.2016.1254350.
Slatina, E., Music, M., Babic, N., Dervisevic, A., Mujaric, E., Salibasic, M., et al. (2013). Correlation between change in air humidity and the incidence of stroke. Materia Socio-medica, 25(4), 242–245. https://doi.org/10.5455/msm.2013.25.242-245.
Sobel, E., Zhang, Z. X., Alter, M., Lai, S. M., Davanipour, Z., Friday, G., et al. (1987). Stroke in the Lehigh Valley: Seasonal variation in incidence rates. Stroke, 18(1), 38–42.
Soomro, A. M., Solangi, A. G., Shaikh, A. B., Gurbakhshni, K., & Mahesar, H. A. (2011). Stroke types in relation to seasonal variation and months of a year. Medical Channel, 17(2), 57–62.
Spengos, K., Vemmos, K. N., Tsivgoulis, G., Synetos, A., Zakopoulos, N., Zis, V. P., et al. (2003). Seasonal variation of hospital admissions caused by acute stroke in Athens, Greece. Journal of Stroke and Cerebrovascular Diseases, 12(2), 93–96. https://doi.org/10.1053/jscd.2003.15.
Stroup, D. F., Berlin, J. A., Morton, S. C., Olkin, I., Williamson, G. D., Rennie, D., et al. (2000). Meta-analysis of observational studies in epidemiology: A proposal for reporting. Meta-analysis of observational studies in epidemiology (MOOSE) group. JAMA, 283(15), 2008–2012.
Takizawa, S., Shibata, T., Takagi, S., Kobayashi, S., & Japan Standard Stroke Registry Study, G. (2013). Seasonal variation of stroke incidence in Japan for 35631 stroke patients in the Japanese Standard Stroke Registry, 1998–2007. Journal of Stroke and Cerebrovascular Diseases, 22(1), 36–41.
Telman, G., Fahoum, S., Sprecher, E., & Kouperberg, E. (2013). Seasonal, monthly, and weekly variations in admissions, in-hospital mortality, and length of stay in acute ischemic stroke in Northern Israel. Journal of Neurology & Translational Neuroscience, 1, 1007.
Tsementzis, S. A., Kennet, R. P., Hitchcock, E. R., Gill, J. S., & Beevers, D. G. (1991). Seasonal variation of cerebrovascular diseases. Acta Neurochirurgica (Wien), 111, 80–83.
Turin, T. C., Kita, Y., Murakami, Y., Rumana, N., Sugihara, H., Morita, Y., et al. (2008). Higher stroke incidence in the spring season regardless of conventional risk factors: Takashima Stroke Registry, Japan, 1988–2001. Stroke, 39(3), 745–752. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.107.495929.
Wang, H., Sekine, M., Chen, X., & Kagamimori, S. (2002). A study of weekly and seasonal variation of stroke onset. International Journal of Biometeorology, 47(1), 13–20. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00484-002-0147-x.
Wang, X., Cao, Y., Hong, D., Zheng, D., Richtering, S., Sandset, E. C., et al. (2016). Ambient temperature and stroke occurrence: A systematic review and meta-analysis. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 13(7), 698. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph13070698.
Wang, Y., Levi, C. R., Attia, J. R., D'Este, C. A., Spratt, N., & Fisher, J. (2003). Seasonal variation in stroke in the hunter region, Australia: A 5-year hospital-based study, 1995–2000. Stroke, 34(5), 1144–1150. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.STR.0000067703.71251.B6.
Woodhouse, P. R., Khaw, K. T., Plummer, M., Foley, A., & Meade, T. W. (1994). Seasonal variations of plasma fibrinogen and factor VII activity in the elderly: winter infections and death from cardiovascular disease. Lancet, 343(8895), 435–439.
Zhong, H., Shu, Z., Zhou, Y., Lu, Y., Yi, B., Tang, X., et al. (2017). Seasonal effect on association between atmospheric pollutants and hospital emergency room visit for stroke. Journal of Stroke and Cerebrovascular Diseases. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2017.08.014.
Ziauddin., Iqbal, N., Shah, I. A., Ali, Z., Rehman, H. U., & Mehmood, K. (2015). Seasonal variation in stroke in a teaching hospital of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa. Journal of Postgraduate Medical Institute, 29(3), 193–198.
Funding
This study was funded by National Key R&D Program of China (2017YFC0907504 and SQ2018YFC130023).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YL made substantial contributions to the study conception, acquisition of data, methodological assessment and main drafting of the manuscript. ZZ performed part of data analysis and drafted the study search and inclusion criteria. NC did another part of data analysis and interpretation. LH and MZ designed and revised the manuscript. All the authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Zhou, Z., Chen, N. et al. Seasonal variation in the occurrence of ischemic stroke: A meta-analysis. Environ Geochem Health 41, 2113–2130 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-019-00265-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-019-00265-y