Abstract
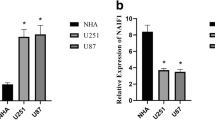
Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) is the most common and lethal type of primary malignant brain tumor. In recent years, increasing reports suggest that discovery of microRNAs (miRNAs) might provide a novel therapeutical target for human cancers, including GBM. The expression and roles of microRNA-183 (miR-183) has been explored in several types of human cancers, including in GBM, and plays important roles in tumor initiation and progression. However, its biological functions in GBM remain largely unknown. In this study, we demonstrated that miR-183 was significantly up-regulated in astrocytoma tissues and glioblastoma cell lines. Introduction of miR-183 mimics into U251 cells could promoted, while its antisense oligos inhibited cell proliferation and invasion. Moreover, we identified neurofilament light polypeptide (NEFL) as a novel target gene of miR-183. The expression levels of NEFL are inversely correlated with that of miR-183 in human astrocytoma clinical specimens. In addition, NEFL-siRNA could significantly attenuate the inhibitory effects of knockdown miR-183 on the proliferation and invasion of U251 cells via mTOR signaling pathway. Overall, This study revealed that miR-183 promotes glioma cell proliferation by targeting NEFL, and also demonstrated that miR-183 could be a potential target for GBM treatment.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bartel DP (2004) MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116:281–297
Chen B, Chen J, House MG, Cullen KJ, Nephew KP, Guo Z (2012) Role of neurofilament light polypeptide in head and neck cancer chemoresistance. Mol Cancer Res 10:305–315
Coon SW, Savera AT, Zarbo RJ, Benninger MS, Chase GA, Rybicki BA, Van Dyke DL (2004) Prognostic implications of loss of heterozygosity at 8p21 and 9p21 in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Cancer 111:206–212
Haddad LA, Smith N, Bowser M, Niida Y, Murthy V, Gonzalez-Agosti C, Ramesh V (2002) The TSC1 tumor suppressor hamartin interacts with neurofilament-L and possibly functions as a novel integrator of the neuronal cytoskeleton. J Biol Chem 277:44180–44186
Kang S, Kim B, Park SB, Jeong G, Kang HS, Liu R, Kim SJ (2013) Stage-specific methylome screen identifies that NEFL is downregulated by promoter hypermethylation in breast cancer. Int J Oncol 43:1659–1665
Knowles MA, Shaw ME, Proctor AJ (1993) Deletion mapping of chromosome 8 in cancers of the urinary bladder using restriction fragment length polymorphisms and microsatellite polymorphisms. Oncogene 8:1357–1364
Lee HK, Finniss S, Cazacu S, Bucris E, Ziv-Av A, Xiang C, Bobbitt K, Rempel SA, Hasselbach L, Mikkelsen T, Slavin S, Brodie C (2013) Mesenchymal stem cells deliver synthetic microRNA mimics to glioma cells and glioma stem cells and inhibit their cell migration and self-renewal. Oncotarget 4:346–361
Leung WK, He M, Chan AW, Law PT, Wong N (2015) Wnt/beta-Catenin activates MiR-183/96/182 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma that promotes cell invasion. Cancer Lett 362:97–105
Li P, Sheng C, Huang L, Zhang H, Huang L, Cheng Z, Zhu Q (2014) MiR-183/-96/-182 cluster is up-regulated in most breast cancers and increases cell proliferation and migration. Breast Cancer Res 16:473
Liu X, Lei Q, Yu Z, Xu G, Tang H, Wang W, Wang Z, Li G, Wu M (2015) MiR-101 reverses the hypomethylation of the LMO3 promoter in glioma cells. Oncotarget 6:7930–7943
Lu J, Getz G, Miska EA, Alvarez-Saavedra E, Lamb J, Peck D, Sweet-Cordero A, Ebert BL, Mak RH, Ferrando AA, Downing JR, Jacks T, Horvitz HR, Golub TR (2005) MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature 435:834–838
Lu YY, Zheng JY, Liu J, Huang CL, Zhang W, Zeng Y (2015) miR-183 induces cell proliferation, migration, and invasion by regulating PDCD4 expression in the SW1990 pancreatic cancer cell line. Biomed Pharmacother 70:151–157
Peng G, Yuan X, Yuan J, Liu Q, Dai M, Shen C, Ma J, Liao Y, Jiang W (2015) miR-25 promotes glioblastoma cell proliferation and invasion by directly targeting NEFL. Mol Cell Biochem 409:103–111
Qiu M, Liu L, Chen L, Tan G, Liang Z, Wang K, Liu J, Chen H (2014) microRNA-183 plays as oncogenes by increasing cell proliferation, migration and invasion via targeting protein phosphatase 2A in renal cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 452:163–169
Ren LH, Chen WX, Li S, He XY, Zhang ZM, Li M, Cao RS, Hao B, Zhang HJ, Qiu HQ, Shi RH (2014) MicroRNA-183 promotes proliferation and invasion in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma by targeting programmed cell death 4. Br J Cancer 111:2003–2013
Ricard D, Idbaih A, Ducray F, Lahutte M, Hoang-Xuan K, Delattre JY (2012) Primary brain tumours in adults. Lancet 379:1984–1996
Stephan C, Jung M, Rabenhorst S, Kilic E, Jung K (2015) Urinary miR-183 and miR-205 do not surpass PCA3 in urine as predictive markers for prostate biopsy outcome despite their highly dysregulated expression in prostate cancer tissue. Clin Chem Lab Med 53:1109–1118
Tanaka H, Sasayama T, Tanaka K, Nakamizo S, Nishihara M, Mizukawa K, Kohta M, Koyama J, Miyake S, Taniguchi M, Hosoda K, Kohmura E (2013) MicroRNA-183 upregulates HIF-1alpha by targeting isocitrate dehydrogenase 2 (IDH2) in glioma cells. J Neurooncol 111:273–283
Tang H, Wang Z, Liu X, Liu Q, Xu G, Li G, Wu M (2012) LRRC4 inhibits glioma cell growth and invasion through a miR-185-dependent pathway. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 12:1032–1042
Tang H, Bian Y, Tu C, Wang Z, Yu Z, Liu Q, Xu G, Wu M, Li G (2013) The miR-183/96/182 cluster regulates oxidative apoptosis and sensitizes cells to chemotherapy in gliomas. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 13:221–231
Tang H, Wang Z, Liu Q, Liu X, Wu M, Li G (2014) Disturbing miR-182 and -381 inhibits BRD7 transcription and glioma growth by directly targeting LRRC4. PLoS One 9:e84146
Wang Z, Yang J, Xu G, Wang W, Liu C, Yang H, Yu Z, Lei Q, Xiao L, Xiong J, Zeng L, Xiang J, Ma J, Li G, Wu M (2015) Targeting miR-381-NEFL axis sensitizes glioblastoma cells to temozolomide by regulating stemness factors and multidrug resistance factors. Oncotarget 6:3147–3164
Wei C, Song H, Sun X, Li D, Song J, Hua K, Fang L (2015) miR-183 regulates biological behavior in papillary thyroid carcinoma by targeting the programmed cell death 4. Oncol Rep 34:211–220
Wen PY, Kesari S (2008) Malignant gliomas in adults. N Engl J Med 359:492–507
Yang M, Liu R, Li X, Liao J, Pu Y, Pan E, Yin L, Wang Y (2014) miRNA-183 suppresses apoptosis and promotes proliferation in esophageal cancer by targeting PDCD4. Mol Cells 37:873–880
Zhang L, Quan H, Wang S, Li X, Che X (2015a) MiR-183 promotes growth of non-small cell lung cancer cells through FoxO1 inhibition. Tumour Biol 36:8121–8126
Zhang Q, Ren W, Huang B, Yi L, Zhu H (2015b) MicroRNA-183/182/96 cooperatively regulates the proliferation of colon cancer cells. Mol Med Rep 12:668–674
Zhu Y, Parada LF (2002) The molecular and genetic basis of neurological tumours. Nat Rev Cancer 2:616–626
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province (Nos. 2015JJ2191 and 2015JJ3161), and the Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education (No. 20130162120083). The authors thank Dr. Gang Peng of Xiangya hospital for his precious suggestions and generous help in carrying out this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts of interest for all authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Zy., Xiong, J., Zhang, Ss. et al. Up-Regulation of microRNA-183 Promotes Cell Proliferation and Invasion in Glioma By Directly Targeting NEFL. Cell Mol Neurobiol 36, 1303–1310 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-016-0328-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-016-0328-5