Abstract
Background
The goal of this study was to assess the value of a urinary biomarker profile comprised of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL), fibroblast growth factor-2 (FGF-2), and epidermal growth factor (EGF), to detect acute kidney injury (AKI) in critically ill neonates.
Methods
We conducted a prospective cohort pilot study of at-risk neonates treated in a level IIIC neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) with therapeutic hypothermia (HT) (n = 25) or extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) (n = 10). Urine was collected at baseline, 48 h of illness, and > 24 h post-recovery of their corresponding treatments. Control samples were collected from 27 healthy newborns. The data were expressed as urinary concentrations and values normalized for urinary creatinine. AKI was defined as the presence of oliguria >24 h and/or elevated serum creatinine (SCr), or the failure to improve the estimated creatinine clearance (eCCL) by >50 % post-recovery. Non-parametric statistical tests and ROC analyses were used to interpret the data.
Results
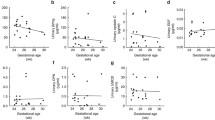
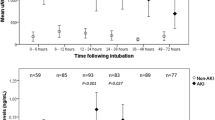
Fifteen at-risk newborns had AKI. In the first 48 h of illness, the urinary levels of NGAL and FGF-2 had high sensitivity but poor specificity to identify neonates with AKI. At recovery, low urinary EGF levels identified neonates with AKI with a sensitivity of 74 % and specificity of 84 %. Overall, in the early stages of a critical illness, the urinary levels of NGAL and FGF-2 were sensitive, but not specific, to identify neonates at risk of AKI. Low EGF levels post-recovery identified critically ill neonates with AKI.
Conclusions
These findings require validation in larger prospective studies.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gupta BD, Sharma P, Bagla J, Parakh M, Soni JP (2005) Renal failure in asphyxiated neonates. Indian Pediatr 42:928–934
Aggarwal A, Kumar P, Chowdhary G, Majumdar S, Narang A (2005) Evaluation of renal functions in asphyxiated newborns. J Trop Pediatr 51:295–299
Karlowicz MG, Adelman RD (1995) Nonoliguric and oliguric acute renal failure in asphyxiated term neonates. Pediatr Nephrol 9:718–722
Selewski DT, Jordan BK, Askenazi DJ, Dechert RE, Sarkar S (2012) Acute kidney injury in asphyxiated newborns treated with therapeutic hypothermia. J Pediatr pii: S0022-3476(12)01149
Askenazi DJ, Ambalavanan N, Hamilton K, Cutter G, Laney D, Kaslow R, Georgeson K, Barnhart DC, Dimmitt RA (2011) Acute kidney injury and renal replacement therapy independently predict mortality in neonatal and pediatric noncardiac patients on extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. Pediatr Crit Care Med 12:e1–e6
Mathur NB, Agarwal HS, Maria A (2006) Acute renal failure in neonatal sepsis. Indian J Pediatr 73:499–502
Agras PI, Tarcan A, Baskin E, Cengiz N, Gurakan B, Saatci U (2004) Acute renal failure in the neonatal period. Ren Fail 26:305–309
Askenazi DJ, Montesanti A, Hunley H, Koralkar R, Pawar P, Shuaib F, Liwo A, Devarajan P, Ambalavanan N (2011) Urine biomarkers predict acute kidney injury and mortality in very low birth weight infants. J Pediatr 159(907–912):e901
Kaur S, Jain S, Saha A, Chawla D, Parmar VR, Basu S, Kaur J (2011) Evaluation of glomerular and tubular renal function in neonates with birth asphyxia. Ann Trop Paediatr 31:129–134
Askenazi DJ, Ambalavanan N, Goldstein SL (2009) Acute kidney injury in critically ill newborns: what do we know? What do we need to learn? Pediatr Nephrol 24:265–274
Drukker A, Guignard JP (2002) Renal aspects of the term and preterm infant: a selective update. Curr Opin Pediatr 14:175–182
Krawczeski CD, Woo JG, Wang Y, Bennett MR, Ma Q, Devarajan P (2011) Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin concentrations predict development of acute kidney injury in neonates and children after cardiopulmonary bypass. J Pediatr 158(1009–1015):e1001
Schmidt-Ott KM (2011) Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin as a biomarker of acute kidney injury–where do we stand today? Nephrol Dial Transplant 26:762–764
Mishra J, Ma Q, Prada A, Mitsnefes M, Zahedi K, Yang J, Barasch J, Devarajan P (2003) Identification of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin as a novel early urinary biomarker for ischemic renal injury. J Am Soc Nephrol 14:2534–2543
Mori K, Lee HT, Rapoport D, Drexler IR, Foster K, Yang J, Schmidt-Ott KM, Chen X, Li JY, Weiss S, Mishra J, Cheema FH, Markowitz G, Suganami T, Sawai K, Mukoyama M, Kunis C, D’Agati V, Devarajan P, Barasch J (2005) Endocytic delivery of lipocalin-siderophore-iron complex rescues the kidney from ischemia-reperfusion injury. J Clin Invest 115:610–621
Parravicini E, Nemerofsky SL, Michelson KA, Huynh TK, Sise ME, Bateman DA, Lorenz JM, Barasch JM (2010) Urinary neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin is a promising biomarker for late-onset culture-positive sepsis in very low birth weight infants. Pediatr Res 67:636–640
Paragas N, Qiu A, Zhang Q, Samstein B, Deng SX, Schmidt-Ott KM, Viltard M, Yu W, Forster CS, Gong G, Liu Y, Kulkarni R, Mori K, Kalandadze A, Ratner AJ, Devarajan P, Landry DW, D’Agati V, Lin CS, Barasch J (2011) The Ngal reporter mouse detects the response of the kidney to injury in real time. Nat Med 17:216–222
Ray P, Acheson D, Chitrakar R, Cnaan A, Gibbs K, Hirschman GH, Christen E, Trachtman H (2002) Basic fibroblast growth factor among children with diarrhea-associated hemolytic uremic syndrome. J Am Soc Nephrol 13:699–707
Ray PE, Liu XH, Xu L, Rakusan T (1999) Basic fibroblast growth factor in HIV-associated hemolytic uremic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 13:586–593
Liu XH, Aigner A, Wellstein A, Ray PE (2001) Up-regulation of a fibroblast growth factor binding protein in children with renal diseases. Kidney Int 59:1717–1728
Soler-Garcia AA, Rakhmanina NY, Mattison PC, Ray PE (2009) A urinary biomarker profile for children with HIV-associated renal diseases. Kidney Int 76:207–214
Tsau YK, Sheu JN, Chen CH, Teng RJ, Chen HC (1996) Decreased urinary epidermal growth factor in children with acute renal failure: epidermal growth factor/creatinine ratio not a reliable parameter for urinary epidermal growth factor excretion. Pediatr Res 39:20–24
Chen L, Liu W (1997) Effect of asphyxia on urinary epidermal growth factor levels in newborns. J Tongi Med Univ 17:144–146
Basile DP (2007) The endothelial cell in ischemic acute kidney injury: implications for acute and chronic function. Kidney Int 72:151–156
Kiley SC, Chevalier RL (2009) Urinary biomarkers: the future looks promising. Kidney Int 76:133–134
Grandaliano G, Gesualdo L, Bartoli F, Ranieri E, Monno R, Leggio A, Paradies G, Caldarulo E, Infante B, Schena FP (2000) MCP-1 and EGF renal expression and urine excretion in human congenital obstructive nephropathy. Kidney Int 58:182–192
Kwon O, Ahn K, Zhang B, Lockwood T, Dhamija R, Anderson D, Saqib N (2010) Simultaneous monitoring of multiple urinary cytokines may predict renal and patient outcome in ischemic AKI. Ren Fail 32:699–708
Askenazi DJ, Koralkar R, Hundley HE, Montesanti A, Parwar P, Sonjara S, Ambalavanan N (2012) Urine biomarkers predict acute kidney injury in newborns. J Pediatr 161(270–275):e271
Shankaran S, Laptook AR, Ehrenkranz RA, Tyson JE, McDonald SA, Donovan EF, Fanaroff AA, Poole WK, Wright LL, Higgins RD, Finer NN, Carlo WA, Duara S, Oh W, Cotten CM, Stevenson DK, Stoll BJ, Lemons JA, Guillet R, Jobe AH (2005) Whole-body hypothermia for neonates with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. N Engl J Med 353:1574–1584
Schwartz GJ, Feld LG, Langford DJ (1984) A simple estimate of glomerular filtration rate in full-term infants during the first year of life. J Pediatr 104:849–854
Huynh TK, Bateman DA, Parravicini E, Lorenz JM, Nemerofsky SL, Sise ME, Bowman TM, Polesana E, Barasch JM (2009) Reference values of urinary neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin in very low birth weight infants. Pediatr Res 66:528–532
Lavery AP, Meinzen-Derr JK, Anderson E, Ma Q, Bennett MR, Devarajan P, Schibler KR (2008) Urinary NGAL in premature infants. Pediatr Res 64:423–428
Parravicini E (2010) The clinical utility of urinary neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin in the neonatal ICU. Curr Opin Pediatr 22:146–150
Ray PE, Tassi E, Liu XH, Wellstein A (2006) Role of fibroblast growth factor-binding protein in the pathogenesis of HIV-associated hemolytic uremic syndrome. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 290:R105–R113
Watanabe K, Ono A, Hirata Y, Fukuda Y, Kojima T, Kobayashi Y (1989) Maturational changes and origin of urinary human epidermal growth factor in the neonatal period. Biol Neonate 56:241–245
Evans NJ, Rutter N, Gregory H (1986) Urinary excretion of epidermal growth factor in the newborn. Early Hum Dev 14:277–282
Di Paolo S, Gesualdo L, Stallone G, Ranieri E, Schena FP (1997) Renal expression and urinary concentration of EGF and IL-6 in acutely dysfunctioning kidney transplanted patients. Nephrol Dial Transplant 12:2687–2693
Mattila AL, Perheentupa J, Pesonen K, Viinikka L (1985) Epidermal growth factor in human urine from birth to puberty. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 61:997–1000
Bagli DJ, Van Savage JG, Khoury AE, Carr M, McLorie GA (1997) Basic fibroblast growth factor in the urine of children with voiding pathology. J Urol 158:1123–1127
Scott SM, Guardian CM, Angelus P, Backstrom C (1991) Developmental pattern of urinary epidermal growth factor in the premature infant and the influence of gender. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 72:588–593
Marler JJ, Fishman SJ, Kilroy SM, Fang J, Upton J, Mulliken JB, Burrows PE, Zurakowski D, Folkman J, Moses MA (2005) Increased expression of urinary matrix metalloproteinases parallels the extent and activity of vascular anomalies. Pediatrics 116:38–45
Kaplan F, Sawyer J, Connors S, Keough K, Shore E, Gannon F, Glaser D, Rocke D, Zasloff M, Folkman J (1998) Urinary basic fibroblast growth factor. A biochemical marker for preosseous fibroproliferative lesions in patients with fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva. Clin Orthop Relat Res 346:59–65
Gupta GK, Milner L, Linshaw MA, McCauley RG, Connors S, Folkman J, Bianchi DW (2000) Urinary basic fibroblast growth factor: a noninvasive marker of progressive cystic renal disease in a child. Am J Med Genet 93:132–135
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by NIH R0-1 HL-102497, R0-1 HL-55605, R0-1 DK-049419 and U54- HD071601.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hoffman, S.B., Massaro, A.N., Soler-García, Á.A. et al. A novel urinary biomarker profile to identify acute kidney injury (AKI) in critically ill neonates: a pilot study. Pediatr Nephrol 28, 2179–2188 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-013-2524-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-013-2524-6