Abstract
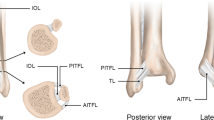
The distal tibiofibular joint is a fibrous joint that plays a crucial role in the stability of the ankle joint. It is stabilized by three main ligaments: the anterior inferior tibiofibular ligament, the posterior inferior tibiofibular ligament, and the interosseous tibiofibular ligament, which are well delineated on magnetic resonance imaging. Pathology of the distal tibiofibular joint is mostly related to trauma and the longer-term complications of trauma, such as soft tissue impingement, heterotopic ossification, and synostosis. This review article outlines the MRI anatomy and pathology of this joint.




















Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
27 December 2019
Unfortunately in Volume 49, Issue 1 had been published online with an incorrect date (2001 instead of 2020).
References
Hermans JJ, Beumer A, de Jong TAW, Kleinrensink G-J. Anatomy of the distal tibiofibular syndesmosis in adults: a pictorial essay with a multimodality approach. J Anat. 2010;217(6):633–45.
Brown KW, Morrison WB, Schweitzer ME, Parellada JA, Nothnagel H. MRI findings associated with distal tibiofibular syndesmosis injury. Am J Roentgenol. 2004;182(1):131–6.
Khazai RS, Weatherford BM. Current strategies in the management of syndesmotic injuries: tech. Foot Ankle Surg. 2018;17(3):126–35.
Ogilvie-Harris DJ, Reed SC, Hedman TP. Disruption of the ankle syndesmosis: biomechanical study of the ligamentous restraints. Arthroscopy. 1994;10(5):558–60.
Clanton TO, Williams BT, Backus JD, Dornan GJ, Liechti DJ, Whitlow SR, et al. Biomechanical analysis of the individual ligament contributions to syndesmotic stability. Foot Ankle Int. 2017;38(1):66–75.
Park YH, Yoon MA, Choi WS, Choi GW, Hong SJ, Kim HJ. The predictive value of MRI in the syndesmotic instability of ankle fracture. Skelet Radiol. 2018;47(4):533–40.
Rammelt S, Zwipp H, Grass R. Injuries to the distal tibiofibular syndesmosis: an evidence-based approach to acute and chronic lesions. Foot Ankle Clin. 2008;13(4):611–33.
Bartonicek J. Anatomy of the tibiofibular syndesmosis and its clinical relevance. Surg Radiol Anat. 2003;25(5–6):379–86.
Boonthathip M, Chen L, Trudell DJ, Resnick DL. Tibiofibular syndesmotic ligaments: MR arthrography in cadavers with anatomic correlation. Radiology. 2010;254(3):827–36.
Clanton TO, Ho CP, Williams BT, Surowiec RK, Gatlin CC, Haytmanek CT, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging characterization of individual ankle syndesmosis structures in asymptomatic and surgically treated cohorts. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2016;24(7):2089–102.
Oae K, Takao M, Naito K, Uchio Y, Kono T, Ishida J, et al. Injury of the tibiofibular syndesmosis: value of MR imaging for diagnosis. Radiology. 2003;227(1):155–61.
Nikolopoulos CE, Tsirikos AI, Sourmelis S, Papachristou G. The accessory anteroinferior tibiofibular ligament as a cause of talar impingement: a cadaveric study. Am J Sports Med. 2004;32(2):389–95.
Subhas N, Vinson EN, Cothran RL, Santangelo JR, Nunley JA, Helms CA. MRI appearance of surgically proven abnormal accessory anterior–inferior tibiofibular ligament (Bassett’s ligament). Skelet Radiol. 2007;37(1):27–33.
Ebraheim NA, Taser F, Shafiq Q, Yeasting RA. Anatomical evaluation and clinical importance of the tibiofibular syndesmosis ligaments. Surg Radiol Anat. 2006;28(2):142–9.
Muhle C, Frank LR, Rand T, Ahn JM, Yeh LR, Trudell D, et al. Tibiofibular syndesmosis: high-resolution MRI using a local gradient coil. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1998;22(6):938–44.
Oh C-S, Won H-S, Hur M-S, Chung I-H, Kim S, Suh J-S, et al. Anatomic variations and MRI of the intermalleolar ligament. Am J Roentgenol. 2006;186(4):943–7.
Carr JC, Werner BC, Yarboro SR. An update on management of syndesmosis injury: a national US database study. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 2016;45(7):E472–7.
Magan A, Golano P, Maffulli N, Khanduja V. Evaluation and management of injuries of the tibiofibular syndesmosis. Br Med Bull. 2014;111(1):101–15.
McCollum GA, van den Bekerom MPJ, Kerkhoffs GMMJ, Calder JDF, van Dijk CN. Syndesmosis and deltoid ligament injuries in the athlete. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2013;21(6):1328–37.
Beumer A, Valstar ER, Garling EH, Niesing R, Ginai AZ, Ranstam J, et al. Effects of ligament sectioning on the kinematics of the distal tibiofibular syndesmosis: a radiostereometric study of 10 cadaveric specimens based on presumed trauma mechanisms with suggestions for treatment. Acta Orthop. 2006;77(3):531–40.
Botchu R, Allen P, Rennie WJ. Isolated posterior high ankle sprain: a report of three cases. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2013;21(3):391–5.
Sikka RS, Fetzer GB, Sugarman E, Wright RW, Fritts H, Boyd JL, et al. Correlating MRI findings with disability in syndesmotic sprains of NFL players. Foot Ankle Int. 2012;33(5):371–8.
Massri-Pugin J, Lubberts B, Vopat BG, Wolf JC, DiGiovanni CW, Guss D. Role of the deltoid ligament in syndesmotic instability. Foot Ankle Int. 2018;39(5):598–603.
Calder JD, Bamford R, Petrie A, McCollum GA. Stable versus unstable grade II high ankle sprains: a prospective study predicting the need for surgical stabilization and time to return to sports. Arthroscopy. 2016;32(4):634–42.
van Putte-Katier N, van Ochten JM, van Middelkoop M, Bierma-Zeinstra SMA, Oei EHG. Magnetic resonance imaging abnormalities after lateral ankle trauma in injured and contralateral ankles. Eur J Radiol. 2015;84(12):2586–92.
Nussbaum ED, Hosea TM, Sieler SD, Incremona BR, Kessler DE. Prospective evaluation of syndesmotic ankle sprains without diastasis. Am J Sports Med. 2001;29(1):31–5.
Krähenbühl N, Weinberg MW, Davidson NP, Mills MK, Hintermann B, Saltzman CL, et al. Imaging in syndesmotic injury: a systematic literature review. Skelet Radiol. 2018;47(5):631–48.
de César PC, Avila EM, de Abreu MR. Comparison of magnetic resonance imaging to physical examination for syndesmotic injury after lateral ankle sprain. Foot Ankle Int. 2011;32(12):1110–4.
Kellett JJ, Lovell GA, Eriksen DA, Sampson MJ. Diagnostic imaging of ankle syndesmosis injuries: a general review. J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol. 2018;62(2):159–68.
Harper MC, Keller TS. A radiographic evaluation of the tibiofibular syndesmosis. Foot Ankle. 1989;10(3):156–60.
Nielson JH, Gardner MJ, Peterson MGE, Sallis JG, Potter HG, Helfet DL, et al. Radiographic measurements do not predict syndesmotic injury in ankle fractures: an MRI study. Clin Orthop. 2005;(436):216–21.
Takao M, Ochi M, Naito K, Iwata A, Kawasaki K, Tobita M, et al. Arthroscopic diagnosis of tibiofibular syndesmosis disruption. Arthroscopy. 2001;17(8):836–43.
Takao M, Ochi M, Oae K, Naito K, Uchio Y. Diagnosis of a tear of the tibiofibular syndesmosis. The role of arthroscopy of the ankle. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2003;85(3):324–9.
Hermans JJ, Wentink N, Beumer A, Hop WCJ, Heijboer MP, Moonen AFCM, et al. Correlation between radiological assessment of acute ankle fractures and syndesmotic injury on MRI. Skelet Radiol. 2012;41(7):787–801.
Nault M-L, Gascon L, Hébert-Davies J, Leduc S, Laflamme GY, Kramer D. Modification of distal tibiofibular relationship after a mild syndesmotic injury. Foot Ankle Spec. 2017;10(2):133–8.
Gardner MJ, Demetrakopoulos D, Briggs SM, Helfet DL, Lorich DG. Malreduction of the tibiofibular syndesmosis in ankle fractures. Foot Ankle Int. 2006;27(10):788–92.
Yeung TW, Chan CYG, Chan WCS, Yeung YN, Yuen MK. Can pre-operative axial CT imaging predict syndesmosis instability in patients sustaining ankle fractures? Seven years’ experience in a tertiary trauma center. Skelet Radiol. 2015;44(6):823–9.
Patel S, Malhotra K, Cullen NP, Singh D, Goldberg AJ, Welck MJ. Defining reference values for the normal tibiofibular syndesmosis in adults using weight-bearing CT. Bone Joint J. 2019;101-B(3):348–52.
Watson BC, Lucas DE, Simpson GA, Berlet GC, Hyer CF. Arthroscopic evaluation of syndesmotic instability in a cadaveric model. Foot Ankle Int. 2015;36(11):1362–8.
Pakarinen H, Flinkkilä T, Ohtonen P, Hyvönen P, Lakovaara M, Leppilahti J, et al. Intraoperative assessment of the stability of the distal tibiofibular joint in supination-external rotation injuries of the ankle: sensitivity, specificity, and reliability of two clinical tests. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011;93(22):2057–61.
Siriwanarangsun P, Bae WC, Statum S, Chung CB. Advanced MRI techniques for the ankle. Am J Roentgenol. 2017;209(3):511–24.
Evans JM, Schucany WG. Radiological evaluation of a high ankle sprain. Proc (Baylor Univ Med Cent). 2006;19(4):402–5.
Chun K-Y, Choi YS, Lee SH, Kim JS, Young KW, Jeong M-S, et al. Deltoid ligament and tibiofibular syndesmosis injury in chronic lateral ankle instability: magnetic resonance imaging evaluation at 3T and comparison with arthroscopy. Korean J Radiol. 2015;16(5):1096.
Van Niekerk C, Van Dyk B. Dynamic ultrasound evaluation of the syndesmosis ligamentous complex and clear space in acute ankle injury, compared to magnetic resonance imaging and surgical findings. South Afr J Radiol [Internet]. 2017 [cited 2018 Nov 9];21(1). Available from: https://sajr.org.za/index.php/sajr/article/view/1191
Nault M-L, Marien M, Hébert-Davies J, Laflamme GY, Pelsser V, Rouleau DM, et al. MRI quantification of the impact of ankle position on syndesmosis anatomy. Foot Ankle Int. 2017;38(2):215–9.
Hermans JJ, Beumer A, Hop WCJ, Moonen AFCM, Ginai AZ. Tibiofibular syndesmosis in acute ankle fractures: additional value of an oblique MR image plane. Skelet Radiol. 2012;41(2):193–202.
Lee SH, Jacobson J, Trudell D, Resnick D. Ligaments of the ankle: normal anatomy with MR arthrography. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1998;22(5):807–13.
Kim M, Choi YS, Jeong MS, Park M, Chun TJ, Kim JS, et al. Comprehensive assessment of ankle syndesmosis injury using 3D isotropic turbo spin-echo sequences: diagnostic performance compared with that of conventional and oblique 3-T MRI. Am J Roentgenol. 2017;208(4):827–33.
Muratlı HH, Biçimoğlu A, Çelebi L, Boyacıgil S, Damgacı L, Tabak AY. Magnetic resonance arthrographic evaluation of syndesmotic diastasis in ankle fractures. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2005;125(4):222–7.
Cerezal L, Abascal F, García-Valtuille R, Canga A. Ankle MR arthrography: how, why, when. Radiol Clin N Am. 2005;43(4):693–707 viii.
Vogl TJ, Hochmuth K, Diebold T, Lubrich J, Hofmann R, Stöckle U, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging in the diagnosis of acute injured distal tibiofibular syndesmosis. Investig Radiol. 1997;32(7):401–9.
Crema MD, Krivokapic B, Guermazi A, Gravilovic P, Popovic N, D’Hooghe P, et al. MRI of ankle sprain: the association between joint effusion and structural injury severity in a large cohort of athletes. Eur Radiol [Internet]. 2019 [cited 2019 May 19]; Available from: http://link.springer.com/10.1007/s00330-019-06156-1
Ryan LP, Hills MC, Chang J, Wilson CD. The lambda sign: a new radiographic indicator of latent syndesmosis instability. Foot Ankle Int. 2014;35(9):903–8.
Han SH, Lee JW, Kim S, Suh J-S, Choi YR. Chronic tibiofibular syndesmosis injury: the diagnostic efficiency of magnetic resonance imaging and comparative analysis of operative treatment. Foot Ankle Int. 2007 Mar;28(3):336–42.
Kim S, Huh Y-M, Song H-T, Lee S-A, Lee J-W, Lee JE, et al. Chronic tibiofibular syndesmosis injury of ankle: evaluation with contrast-enhanced fat-suppressed 3D fast spoiled gradient-recalled acquisition in the steady state MR imaging. Radiology. 2007;242(1):225–35.
Akseki D, Pinar H, Yaldiz K, Akseki NG, Arman C. The anterior inferior tibiofibular ligament and talar impingement: a cadaveric study. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2002;10(5):321–6.
van den Bekerom MPJ, Raven EEJ. The distal fascicle of the anterior inferior tibiofibular ligament as a cause of tibiotalar impingement syndrome: a current concepts review. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2007;15(4):465–71.
Donovan A, Rosenberg ZS. MRI of ankle and lateral hindfoot impingement syndromes. Am J Roentgenol. 2010;195(3):595–604.
Cha SD, Kim HS, Chung ST, Yoo JH, Park JH, Kim JH, et al. Intra-articular lesions in chronic lateral ankle instability: comparison of arthroscopy with magnetic resonance imaging findings. Clin Orthop Surg. 2012;4(4):293.
Schaffler GJ, Tirman PFJ, Stoller DW, Genant HK, Ceballos C, Dillingham MF. Impingement syndrome of the ankle following supination external rotation trauma: MR imaging findings with arthroscopic correlation. Eur Radiol. 2003;13(6):1357–62.
Botchu R, Douis H, Davies AM, James SL, Puls F, Grimer R. Post-traumatic heterotopic ossification of distal tibiofibular syndesmosis mimicking a surface osteosarcoma. Clin Radiol. 2013;68(12):e676–9.
Sureka J, Jakkani RK, Ahmed M, Panwar S, Shanker S. Congenital distal tibiofibular synostosis. Radiol Case Rep. 2012;7(2):555.
Karasick D, Schweitzer ME, O’Hara BJ. Distal fibular notch: a frequent manifestation of the rheumatoid ankle. Skelet Radiol. 1997;26(9):529–32.
Mavrogenis AF, Papaparaskeva KT, Galanakos S, Papagelopoulos PJ. Pigmented villonodular synovitis of the distal tibiofibular joint: a case report. Clin Podiatr Med Surg. 2011;28(3):589–97.
Acknowledgements
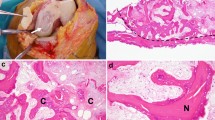
We thank Dr. Samuel Burnand for his valuable comments on an earlier version of the manuscript. We thank Dr. Asad Shah for Figure 11.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sharif, B., Welck, M. & Saifuddin, A. MRI of the distal tibiofibular joint. Skeletal Radiol 49, 1–17 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-019-03260-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-019-03260-7