Abstract
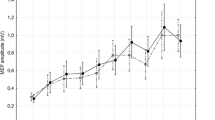
Habituation, i.e. the decremental response to repeated sensorial stimulation, is studied in humans through evoked potential stimulation. Mechanisms underlying habituation are not yet cleared, even if inhibitory circuits are supposed to play an important role. Light deprivation (LD) increases visual cortical excitability likely through down-regulation of GABA circuits. We previously found that high-frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (hf-rTMS) can revert these facilitatory effects likely restoring the activity of inhibitory circuits. Here, we studied the effects of LD and rTMS on habituation of visual evoked potentials (VEPs). The hypothesis was that if the inhibitory circuits have a role in habituation, then LD that downregulates GABA circuits, should impair habituation that in turn should be restored by hf-rTMS. Fifteen healthy subjects underwent VEPs recording in baseline (without LD), in LD alone (without rTMS), in LD and 1 Hz rTMS and in LD and 10 Hz rTMS. Habituation observed in baseline (without LD) was significantly impaired after LD; 10 Hz but not 1 Hz rTMS was able to restore normal habituation phenomena. VEPs habituation is impaired by LD but it could be restored if hf-rTMS is given during LD. As LD acts reducing GABA circuits activity and hf-rTMS likely upregulates such circuits, these data give support to the hypothesis that cortical inhibition can play a relevant role in mechanisms underlying habituation.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Afra J, Proietti Cecchini A, De Pasqua V, Albert A, Schoenen J (1998) Visual evoked potentials during long periods of patternreversal stimulation in migraine. Brain 121:233–241
Aurora SK, al-Sayeed F, Welch KM (1999) The cortical silent period is shortened in migraine with aura. Cephalalgia 19:708–712
Berardelli A, Inghilleri M, Gilio F, Romeo S, Pedace F, Curra A, Manfredi M (1999) Effects of repetitive cortical stimulation on the silent period evoked by magnetic stimulation. Exp Brain Res 125:82–86
Bohotin V, Fumal A, Vandenheede M, Gerard P, Bohotin C, Maertens de Noordhout A, Schoenen J (2002) Effects of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation on visual evoked potentials in migraine. Brain 125:912–922
Boroojerdi B, Bushara KO, Corwell B, Immisch I, Battaglia F, Muellbacher W, Cohen LG (2000) Enhanced excitability of the human visual cortex induced by short-term light deprivation. Cereb Cortex 10:529–534
Boroojerdi B, Battaglia F, Muellbacher W, Cohen LG (2001) Mechanisms underlying rapid experience-dependent plasticity in the human visual cortex. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:14698–14701
Brighina F, Piazza A, Daniele O, Fierro B (2002) Modulation of visual cortical excitability in migraine with aura: effects of 1 Hz repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation. Exp Brain Res 145:177–181
Brighina F, Giglia G, Scalia S, Francolini M, Palermo A, Fierro B (2005) Facilitatory effects of 1 Hz rTMS in motor cortex of patients affected by migraine with aura. Exp Brain Res 161:34–38
Brighina F, Palermo A, Fierro B (2009) Cortical inhibition and habituation to evoked potentials: relevance for pathophysiology of migraine. J Headache Pain 10:77–84
Brighina F, Palermo A, Daniele O, Aloisio A, Fierro B (2010) High-frequency transcranial magnetic stimulation on motor cortex of patients affected by migraine with aura: a way to restore normal cortical excitability? Cephalalgia 30:46–52
Cantello R, Tarletti R, Civardi C (2002) Transcranial magnetic stimulation and Parkinson’s disease. Brain Res Rev 38:309–327
Coppola G, Pierelli F, Schoenen J (2007) Is the cerebral cortex hyperexcitable or hyperresponsive in migraine? Cephalalgia 27:1427–1439
Coppola G, Pierelli F, Schoenen J (2009) Habituation and migraine. Neurobiol Learn Mem 92:249–259
Curra A, Pierelli F, Coppola G, Barbanti P, Buzzi MG, Galeotti F, Serrao M, Truini A, Casal C, Pauri F, Cruccu G (2007) Shortened cortical silent period in facial muscles of patients with migraine. Pain 132:124–131
de Tommaso M (2008) Laser-evoked potentials in primary headaches and cranial neuralgias. Expert Rev Neurother. 8:1339–1345 Review
Fierro B, Ricci R, Piazza A, Scalia S, Giglia G, Vitello G, Brighina F (2003) 1 Hz rTMS enhances extrastriate cortex activity in migraine: evidence of a reduced inhibition? Neurology 61:1446–1448
Fierro B, Brighina F, Vitello G, Piazza A, Scalia S, Giglia G, Daniele O, Pascual-Leone A (2005) Modulatory effects of low- and high-frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation on visual cortex of healthy subjects undergoing light deprivation. J Physiol 565:659–665
Fierro B, Brighina F, D’Amelio M, Daniele O, Lupo I, Ragonese P, Palermo A, Savettieri G (2008) Motor intracortical inhibition in PD: L-DOPA modulation of high-frequency rTMS effects. Exp Brain Res 184:521–528
Fumal A, Coppola G, Bohotin V, Gerardy PY, Seidel L, Donneau AF, Vandenheede M, Maertens de Noordhout A, Schonen J (2006) Induction of long-lasting changes of visual cortex excitability by five daily sessions of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) in healthy volunteers and migraine patients. Cephalalgia 26:143–149
Gilio F, Currà A, Inghilleri M, Lorenzano C, Manfredi M, Berardelli A (2002) Repetitive magnetic stimulation of cortical motor areas in Parkinson’s disease: implications for the pathophysiology of cortical function. Mov Disord 17:467–473
Jacobs KM, Donoghue JP (1991) Reshaping the cortical motor map by unmasking latent intracortical connections. Science 251:944–947
Jones EG (1993) GABAergic neurons and their role in cortical plasticity in primates. Cereb Cortex 3:361–372
Kandel ER, Schwartz JH, Jessell TM (2000) [1981] Principles of Neural Science, 4th edn. McGraw-Hill, New York
Kilman V, van Rossum MC, Turrigiano GG (2002) Activity deprivation reduces miniature IPSC amplitude by decreasing the number of postsynaptic GABA(A) receptors clustered at neocortical synapses. J Neruosci 22:1328–1337
Lefaucheur JP, Drouot X, Ménard-Lefaucheur I, Keravel Y, Nguyen JP (2006) Motor cortex rTMS restores defective intracortical inhibition in chronic neuropathic pain. Neurology 67:1568–1574
Leon-Sarmiento FE, Bara-Jimenez W, Wassermann EM (2005) Visual deprivation effects on human motor cortex excitability. Neurosci Lett 389:17–20
Megela AL, Teyler TJ (1979) Habituation and the human evoked potential. J Comp Physiol Psycol 93:1154–1170
Mulleners WM, Chronicle EP, Vredeveld JW, Koehler PJ (2002) Visual cortex excitability in migraine before and after valproate prophylaxis: a pilot study using TMS. Eur J Neurol 9:35–40
Palmer JE, Chronicle EP, Rolan P, Mulleners WM (2000) Cortical hyperexcitability is cortical under-inhibition: evidence from a novel functional test of migraine patients. Cephalalgia 20:525–532
Pfurtscheller G, Stancak A Jr, Neuper C (1996) Event-related synchronization (ERS) in the alpha band-an electrophysiological correlate of cortical idling: a review. Int J Psychophysiol 24:39–46
Pitskel NB, Merabet LB, Ramos-Estebanez C, Kauffman T, Pascual-Leone A (2007) Timedependent changes in cortical excitability after prolonged visual deprivation. Neuroreport 18:1703–1707
Sanes JN, Donoghue JP (1997) Static and dynamic organization of motor cortex. Adv Neurol 73:277–296
Sappey-Marinier D, Calabrese G, Fein G, Hugg JW, Biggins C, Weiner MW (1992) Effect of photic stimulation on human visual cortex lactate and phosphates using 1H and 31P magnetic resonance spectroscopy. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 12:584–592
Schoenen J (1996) Deficient habituation of evoked cortical potentials in migraine: a link between brain biology, behavior and trigeminovascular activation? Biomed Pharmacother 50:71–78
Siebner HR, Mentschel C, Auer C, Lehner C, Conrad B (2000) Repetitive transcranial megnetic stimulation causes a short-term increase in the duration of the cortical silent period in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Neurosci Lett 284:147–150
Siebner HR, Lang N, Rizzo V, Nitsche MA, Paulus W, Lemon RN, Rothwell JC (2004) Preconditioning of low-frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation with transcranial direct current stimulation: evidence for homeostatic plasticity in the human motor cortex. J Neurosci 24:3379–3385
Valeriani M, de Tommaso M, Restuccia D, Le Pera D, Guido M, Iannetti GD, Libro G, Truini A, Di Trapani G, Puca F, Tonali P, Cruccu G (2003) Reduced habituation to experimental pain in migraine patients: a CO(2) laser evoked potential study. Pain 105:57–64
Ziemann U, Corwell B, Cohen LG (1998a) Modulation of plasticity in human motor cortex after forearm ischemic nerve block. J Neurosci 18:1115–1123
Ziemann U, Hallett M, Cohen LG (1998b) Mechanisms of deafferentation-induced plasticity in human motor cortex. J Neurosci 18:7000–7007
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Palermo, A., Giglia, G., Vigneri, S. et al. Does habituation depend on cortical inhibition? Results of a rTMS study in healthy subjects. Exp Brain Res 212, 101–107 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-011-2701-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-011-2701-4