Abstract
Objective
Severe forms of Kawasaki disease (KD) associated with shock have recently been reported in which a greater number of coronary artery abnormalities (CAA) were observed. In this study, we analyzed organ involvement not restricted to cardiovascular aspects in severe KD and assessed whether their outcome is different than in common forms.
Design
Retrospective study.
Setting
A 12-bed pediatric intensive care unit (PICU) in a university hospital setting.
Patients
All patients managed in the PICU with a diagnosis of KD from 1 January 2001 to 30 April 2009.
Results
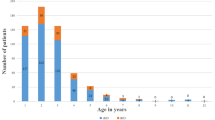
Eleven patients were admitted because of moderate febrile shock without initial KD diagnosis. Median age was 75 months (6–175) with a male:female ratio of 1.4. KD was diagnosed and treated after a delay of 1 day (0–2), for a total of 7 days (5–9) after fever onset. Seven patients (63%) developed CAA after 21 days (6–30) with complete regression within a delay of 120 days (18–240). Nonspecific encephalopathy (n = 6) as well as acute kidney injury (n = 10) were also observed. Multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS) occurred in eight patients. Although predicted mortality according to the PELOD score [21 (10–43)] ranged from 20% to up to 50%, all 11 children survived with no sequelae.
Conclusion
Moderate shock is the main reason for PICU admission in children suffering from KD. These forms can be associated with surprising MODS. Despite the severity of symptoms, all patients survived without any sequelae, hence the need for proper diagnosis and rapid treatment of these unusual severe forms.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kawasaki T (1967) Acute febrile mucocutaneous syndrome with lymphoid involvement with specific. Arerugi 16:78–222
Nakamura Y, Yashiro M, Uehara R, Oki I, Watanabe M, Yanagawa H (2008) Epidemiologic features of Kawasaki disease in Japan: results from the nationwide. J Epidemiol 18:167–172
Bourrillon A (2008) Kawasaki’s disease: multiple and various aspects. Arch Pediatr 15:825–828
Kato H, Sugimura T, Akagi T, Sato N, Hashino K, Maeno Y, Kazue T, Eto G, Yamakawa R (1996) Long-term consequences of Kawasaki disease. A 10 to 21-year follow-up study of 594 patients. Circulation 94:1379–1385
Dajani A, Taubert K, Gerber M, Ferrieri P, Freed M, Takahashi M, Bierman FZ, Karchmer AW, Wilson W (1993) Diagnosis and therapy of Kawasaki disease in children. Circulation 87:1776–1780
Kanegaye JT, Wilder MS, Molkara D, Frazer JR, Pancheri J, Tremoulet AH, Watson VE, Best BM, Burns JC (2009) Recognition of a Kawasaki disease shock syndrome. Pediatrics 123:e783–e789
Dominguez SR, Friedman K, Seewald R, Anderson MS, Willis L, Glodé MP (2008) Kawasaki disease in a pediatric intensive care unit: a case-control study. Pediatrics 122:e786–e790
Newburger JW, Takahashi M, Gerber MA, Gewitz MH, Tani LY, Burns JC, Shulman ST, Bolger AF, Ferrieri P, Baltimore RS, Wilson WR, Baddour LM, Levison ME, Pallasch TJ, Falace DA, Taubert KA, Committee on Rheumatic Fever, Endocarditis, and Kawasaki Disease, Council on Cardiovascular Disease in the Young, American Heart Association (2004) Diagnosis, treatment, and long-term management of Kawasaki disease: a statement. Pediatrics 114:1708–1733
Gorelick M, Shaw K, Baker M (1993) Effect of ambient temperature on capillary refill in healthy children. Pediatrics 92:699–702
Lacroix J, Gauthier M, Hubert P, Leclerc F, Gaudreault P (2007) Urgences et soins intensifs pédiatriques. Surveillance cardiorespiratoire (2ème édition) Masson CHU Sainte-Justine, pp 3–33
Cooper L Jr (2009) Myocarditis. N Engl J Med 360:1526–1538
Carcillo J, Fields A (2002) Clinical practice parameters for hemodynamic support of pediatric and neonatal patients in septic shock. Crit Care Med 30:1365–1378
Fleming S, Thompson M, Stevens R, Heneghan C, Plüddemann A, Maconochie I, Tarassenko L, Mant D (2011) Normal ranges of heart rate and respiratory rate in children from birth to 18 years of age: a systematic review of observational studies. Lancet 377(9770):1011–1018
Teague WG (2003) Noninvasive ventilation in the pediatric intensive care unit for children with acute respiratory failure. Pediatr Pulmonol 35(6):418–426
Akcan-Arikan A, Zappitelli M, Loftis LL, Washburn KK, Jefferson LS, Goldstein SL (2007) Modified RIFLE criteria in critically ill children with acute kidney injury. Kidney Int 71:1028–1035
International Study of Kidney Disease in Children (1978) Nephrotic syndrome in children: prediction of histopathology from clinical and laboratory characteristics at time of diagnosis. A report of the international study of kidney disease in children. Kidney Int 13:159–165
Goldstein B, Giroir B, Randolph A, International Consensus Conference on Pediatric Sepsis (2005) International pediatric sepsis consensus conference: definitions for sepsis and organ dysfunction in pediatrics. Pediatr Crit Care Med 6(1):2–8
Research Committee on Kawasaki Disease (1984) Report of Subcommittee on Standardization of Diagnostic Criteria and Reporting of Coronary Artery Lesions in Kawasaki Disease. Japanese Ministry of Health and Welfare, Tokyo
Leteurtre S, Martinot A, Duhamel A, Proulx F, Grandbastien B, Cotting J, Gottesman R, Joffe A, Pfenninger J, Hubert P, Lacroix J, Leclerc F (2003) Validation of the pediatric logistic organ dysfunction (PELOD) score. Lancet 362:192–197
Dellinger RP, Levy MM, Carlet JM, Bion J, Parker MM, Jaeschke R, Reinhart K, Angus DC, Brun-Buisson C, Beale R, Calandra T, Dhainaut JF, Gerlach H, Harvey M, Marini JJ, Marshall J, Ranieri M, Ramsay G, Sevransky J, Thompson BT, Townsend S, Vender JS, Zimmerman JL, Vincent JL, International Surviving Sepsis Campaign Guidelines Committee, American Association of Critical-Care Nurses, American College of Chest Physicians, American College of Emergency Physicians, Canadian Critical Care Society, European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases, European Respiratory Society, Japanese Association for Acute Medicine, Society of Critical Care Medicine, Surgical Infection Society (2008) International guidelines for management of severe sepsis and septic shock. Crit Care Med 36(1):296–327
Gamillscheg A, Zobel G, Karpf EF, Dacar D, Beitzke A, Stein JI, Suppan C (1993) Atypical presentation of Kawasaki disease in an infant. Pediatr Cardiol 14:223–226
Davies HD, Kirk V, Jadavji T, Kotzin BL (1996) Simultaneous presentation of Kawasaki disease and toxic shock syndrome in an infant. Pediatr Infect Dis J 15:1136–1138
Thabet F, Bafaqih H, Al-Mohaimeed S, Al-Hilali M, Al-Sewairi W, Chehab M (2011) Shock: an unusual presentation of Kawasaki disease. Eur J Pediatr 170:941–943
Fuse S, Tomita H, Ohara T, Iida K, Takamuro M (2003) Severely damaged aortic valve and cardiogenic shock in an infant with Kawasaki disease. Pediatr Int 45:110–113
Rhodes J, King ME, Thomas Aretz H (1998) Case records of the Massachusetts General Hospital. Weekly clinicopathological. Case 36–1998—An 11-year-old girl with fever, hypotension, and azotemia. N Engl J Med 339:1619–1626
Kim M, Kim K (1999) Elevation of cardiac troponin I in the acute stage of Kawasaki disease. Pediatr Cardiol 20:184–188
Marcella JJ, Ursell PC, Goldberger M, Lovejoy W, Fenoglio JJ Jr, Weiss MB (1983) Kawasaki syndrome in an adult: endomyocardial histology and ventricular function. J Am Coll Cardiol 12:374–378
Fujiwara H, Hamashima Y (1978) Pathology of the heart in Kawasaki disease. Pediatrics 61:100–107
Newburger JW, Sanders SP, Burns JC, Parness IA, Beiser AS, Colan SD (1989) Left ventricular contractility and function in Kawasaki syndrome. Effect of intravenous gamma-globulin. Circulation 79:1237–1246
Lemura M, Ishii M, Sugimura T, Akagi T, Kato H (2000) Long term consequences of regressed coronary aneurysms after Kawasaki disease. Heart 83:307–311
Terasawa K, Ichinose E, Matsuishi T, Kato H (1983) Neurological complications in Kawasaki disease. Brain Dev 5:371–374
Ichiyama T, Nishikawa M, Hayashi T, Koga M, Tashiro N, Furukawa S (1998) Cerebral hypoperfusion during acute Kawasaki disease. Stroke 29:1320–1321
Tabarki B, Mahdhaoui A, Selmi H, Yacoub M, Essoussi AS (2001) Kawasaki disease with predominant central nervous system involvement. Pediatr Neurol 25:239–241
Husain E, Hoque E (2006) Meningoencephalitis as a presentation of Kawasaki disease. J Child Neurol 21:1080–1081
Lee BW, Yap HK, Yip WC, Giam YC, Tay JS (1989) Nephrotic syndrome in Kawasaki disease. Aust Paediatr J 25:241–242
Veiga PA, Pieroni D, Baier W, Feld LG (1992) Association of Kawasaki disease and interstitial nephritis. Pediatr Nephrol 6:421–423
Nardi PM, Haller JO, Friedman AP, Slovis TL, Schaffer RM (1985) Renal manifestations of Kawasaki’s disease. Pediatr Radiol 15:116–118
Mac Ardle BM, Chambers TL, Weller SD, Tribe CR (1983) Acute renal failure in Kawasaki disease. J R Soc Med 7:615–616
Salcedo J, Greenberg L, Kapur S (1988) Renal histology of mucocutaneous lymph node syndrome (Kawasaki disease). Clin Nephrol 29:47–51
Zulian F, Falcini F, Zancan L, Martini G, Secchieri S, Luzzatto C, Zacchello F (2003) Acute surgical abdomen as presenting manifestation of Kawasaki disease. J Pediatr 142(6):731–735
Singh R, Ward C, Walton M, Persad R (2007) Atypical Kawasaki disease and gastrointestinal manifestations. Paediatr Child Health 12(3):235–237
Acknowledgments
We thank Prof. G. Cheron and Prof. I. Desguerre (Hôpital Necker-Enfants Malades, Assistance Publique–Hôpitaux de Paris) for their kind assistance (France); and Mr. Pierre Pothier for his critical review of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gatterre, P., Oualha, M., Dupic, L. et al. Kawasaki disease: an unexpected etiology of shock and multiple organ dysfunction syndrome. Intensive Care Med 38, 872–878 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-012-2473-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-012-2473-8